Hepatitis C virus/HIV coinfection and responses to initial antiretroviral treatment
- PMID: 23921611
- PMCID: PMC4214386
- DOI: 10.1097/01.aids.0000432470.46379.dd
Hepatitis C virus/HIV coinfection and responses to initial antiretroviral treatment
Abstract
Objective: To explore the relationship between hepatitis C virus (HCV)/HIV coinfection and responses to initial antiretroviral treatment (ART).
Methods: Four AIDS Clinical Trials Group HIV treatment studies' data were combined to compare initial ART responses between HCV/HIV-coinfected and HIV-monoinfected patients as evaluated by virologic failure, CD4 cell measures, occurrence of AIDS/death and grade 3/4 safety events, using Kaplan-Meier estimates and proportional hazard, regression and mixed effects models, adjusting for baseline covariates.
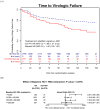
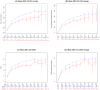
Results: Of the 3041 included participants, 81% were men, 19% had prior history of AIDS, the median (25th, 75th percentile) baseline HIV RNA was 4.72 (4.38-5.18) log10 copies/ml, and the median (25th, 75th percentile) baseline CD4 cell count was 216.0 (76.5-327.0) cells/μl. The 279 HCV/HIV-coinfected individuals were older (44 vs. 37 years), more likely to be black non-Hispanic (47 vs. 36%), and previous/current intravenous drug user (52 vs. 5%) than the 2762 HIV-monoinfected patients (all P values <0.001). HCV/HIV coinfection was associated with earlier virologic failure, hazard ratio (95% confidence interval): 1.43 (1.07-1.91); smaller mean CD4 cell increase and CD4% increase [-33.8 (-52.2 to -15.4) cells/μl and -1.16% (-1.43 to -0.89%), respectively] over a median of 132 weeks of follow-up; earlier occurrence of grade 3/4 safety event, hazard ratio 1.51 (1.26-1.81); and increased AIDS/mortality, hazard ratio 2.10 (1.31-3.37). Treatment effects comparing antiretroviral regimens were not significantly different by HCV/HIV coinfection status.
Conclusion: HCV/HIV coinfection is associated with attenuated response to ART. Results support earlier initiation of HIV therapy and increased monitoring of those initiating ART with HCV/HIV coinfection.
Figures
References
-
- Sherman KE, Rouster SD, Chung RT, Rajicic N. Hepatitis C Virus Prevalence among Patients Infected with Human Immunodeficiency Virus: A Cross-Sectional Analysis of the US Adult AIDS Clinical Trials Group. Clinical Infectious Disease. 2002;34:831–837. - PubMed
-
- Potter M, Odueyungbo A, Yang H, Saeed S, Klein MB. Impact of hepatitis C viral replication on CD4 T-lymphocyte progression in HIV-HCV coinfection before and after antiretroviral therapy. AIDS. 2010;24:1857–1865. - PubMed
-
- Pineda J, Romero-Gómez M, Díaz-García F, Girón-González J, Montero J, Torre-Cisneros J, et al. HIV coinfection shortens the survival of patients with hepatitis C virus-related decompensated cirrhosis. Hepatology. 2005;41:779–89. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

