MicroRNA expression changes during interferon-beta treatment in the peripheral blood of multiple sclerosis patients
- PMID: 23921681
- PMCID: PMC3759901
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms140816087
MicroRNA expression changes during interferon-beta treatment in the peripheral blood of multiple sclerosis patients
Abstract
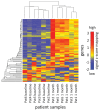
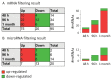
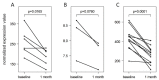
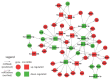
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small non-coding RNA molecules acting as post-transcriptional regulators of gene expression. They are involved in many biological processes, and their dysregulation is implicated in various diseases, including multiple sclerosis (MS). Interferon-beta (IFN-beta) is widely used as a first-line immunomodulatory treatment of MS patients. Here, we present the first longitudinal study on the miRNA expression changes in response to IFN-beta therapy. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) were obtained before treatment initiation as well as after two days, four days, and one month, from patients with clinically isolated syndrome (CIS) and patients with relapsing-remitting MS (RRMS). We measured the expression of 651 mature miRNAs and about 19,000 mRNAs in parallel using real-time PCR arrays and Affymetrix microarrays. We observed that the up-regulation of IFN-beta-responsive genes is accompanied by a down-regulation of several miRNAs, including members of the mir-29 family. These differentially expressed miRNAs were found to be associated with apoptotic processes and IFN feedback loops. A network of miRNA-mRNA target interactions was constructed by integrating the information from different databases. Our results suggest that miRNA-mediated regulation plays an important role in the mechanisms of action of IFN-beta, not only in the treatment of MS but also in normal immune responses. miRNA expression levels in the blood may serve as a biomarker of the biological effects of IFN-beta therapy that may predict individual disease activity and progression.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-29b variants and MxA expression change during interferon beta therapy in patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis.Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2019 Oct;35:241-245. doi: 10.1016/j.msard.2019.07.034. Epub 2019 Jul 31. Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2019. PMID: 31421628
-
miR-145 and miR20a-5p Potentially Mediate Pleiotropic Effects of Interferon-Beta Through Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Signaling Pathway in Multiple Sclerosis Patients.J Mol Neurosci. 2017 Jan;61(1):16-24. doi: 10.1007/s12031-016-0851-3. Epub 2016 Oct 17. J Mol Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 27752929
-
Small non-coding RNA signature in multiple sclerosis patients after treatment with interferon-β.BMC Med Genomics. 2014 May 17;7:26. doi: 10.1186/1755-8794-7-26. BMC Med Genomics. 2014. PMID: 24885345 Free PMC article.
-
An inventory of short term and long term changes in gene expression under interferon β treatment of relapsing remitting MS patients.Curr Pharm Des. 2012;18(29):4475-84. doi: 10.2174/138161212802502215. Curr Pharm Des. 2012. PMID: 22612748 Review.
-
Expression, regulation and function of microRNAs in multiple sclerosis.Int J Med Sci. 2014 Jun 2;11(8):810-8. doi: 10.7150/ijms.8647. eCollection 2014. Int J Med Sci. 2014. PMID: 24936144 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Glatiramer acetate treatment effects on gene expression in monocytes of multiple sclerosis patients.J Neuroinflammation. 2013 Oct 17;10:126. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-10-126. J Neuroinflammation. 2013. PMID: 24134771 Free PMC article.
-
Discovering miRNAs Associated With Multiple Sclerosis Based on Network Representation Learning and Deep Learning Methods.Front Genet. 2022 May 17;13:899340. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.899340. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35656318 Free PMC article.
-
The concerted actions of microRNA-29a and interferon-β modulate complete Freund's adjuvant-induced inflammatory pain by regulating the expression of type 1 interferon receptor, interferon-stimulated gene 15, and p-extracellular signal-regulated kinase.BJA Open. 2025 Feb 3;13:100376. doi: 10.1016/j.bjao.2024.100376. eCollection 2025 Mar. BJA Open. 2025. PMID: 39980495 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating microRNAs as biomarkers for rituximab therapy, in neuromyelitis optica (NMO).J Neuroinflammation. 2016 Jul 8;13(1):179. doi: 10.1186/s12974-016-0648-x. J Neuroinflammation. 2016. PMID: 27393339 Free PMC article.
-
An Overview of Circular RNAs and Their Implications in Myotonic Dystrophy.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Sep 6;20(18):4385. doi: 10.3390/ijms20184385. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31500099 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Compston A., Coles A. Multiple sclerosis. Lancet. 2008;372:1502–1517. - PubMed
-
- Miller D.H., Chard D.T., Ciccarelli O. Clinically isolated syndromes. Lancet Neurol. 2012;11:157–169. - PubMed
-
- Vosoughi R., Freedman M.S. Therapy of MS. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2010;112:365–385. - PubMed
-
- Buck D., Hemmer B. Treatment of multiple sclerosis: Current concepts and future perspectives. J. Neurol. 2011;258:1747–1762. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

