Post-transcriptional regulation by poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation of the RNA-binding proteins
- PMID: 23921685
- PMCID: PMC3759905
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms140816168
Post-transcriptional regulation by poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation of the RNA-binding proteins
Abstract
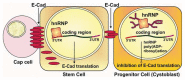
Gene expression is intricately regulated at the post-transcriptional level by RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) via their interactions with pre-messenger RNA (pre-mRNA) and mRNA during development. However, very little is known about the mechanism regulating RBP activities in RNA metabolism. During the past few years, a large body of evidence has suggested that many RBPs, such as heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins (hnRNPs), undergo post-translational modification through poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation to modulate RNA processing, including splicing, polyadenylation, translation, miRNA biogenesis and rRNA processing. Accordingly, RBP poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation has been shown to be involved in stress responses, stem cell differentiation and retinal morphogenesis. Here, we summarize recent advances in understanding the biological roles of RBP poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation, as controlled by Poly(ADP-ribose) Polymerases (PARPs) and Poly(ADP-ribose) Glycohydrolase (PARG). In addition, we discuss the potential of PARP and PARG inhibitors for the treatment of RBP-related human diseases, including cancer and neurodegenerative disorders.
Figures

References
-
- Houseley J., Tollervey D. The many pathways of RNA degradation. Cell. 2009;136:763–776. - PubMed
-
- Keene J.D. RNA regulons: Coordination of post-transcriptional events. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2007;8:533–543. - PubMed
-
- Änkö M.-L., Neugebauer K.M. RNA-protein interactions in vivo: Global gets specific. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2012;37:255–262. - PubMed
-
- Lukong K.E., Chang K.W., Khandjian E.W., Richard S. RNA-binding proteins in human genetic disease. Trends Genet. 2008;24:416–425. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

