Reference region automatic extraction in dynamic [(11)C]PIB
- PMID: 23921900
- PMCID: PMC3824180
- DOI: 10.1038/jcbfm.2013.133
Reference region automatic extraction in dynamic [(11)C]PIB
Abstract
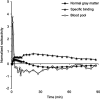
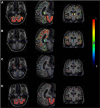
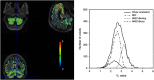
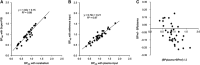
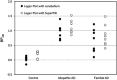
The positron emission tomography (PET) radiotracer [(11)C]Pittsburgh Compound B (PIB) is a marker of amyloid plaque deposition in brain, and binding potential is usually quantified using the cerebellum as a reference where the specific binding is negligible. The use of the cerebellum as a reference, however, has been questioned by the reported cerebellar [(11)C]PIB retention in familial Alzheimer's disease (AD) subjects. In this work, we developed a supervised clustering procedure for the automatic extraction of a reference region in [(11)C]PIB studies. Supervised clustering models each gray matter voxel as the linear combination of three predefined kinetic classes, normal and lesion gray matter, and blood pool, and extract reference voxels in which the contribution of the normal gray matter class is high. In the validation with idiopathic AD subjects, supervised clustering extracted reference voxels mostly in the cerebellum that indicated little specific [(11)C]PIB binding, and total distribution volumes of the extracted region were lower than those of the cerebellum. Next, the methodology was applied to the familial AD cohort where the cerebellar amyloid load had been demonstrated previously, resulting in higher binding potential compared with that obtained with the cerebellar reference. The supervised clustering method is a useful tool for the accurate quantification of [(11)C]PIB studies.
Figures

References
-
- Klunk WE, Engler H, Nordberg A, Wang Y, Blomqvist G, Holt DP, et al. Imaging brain amyloid in Alzheimer's disease with Pittsburgh compound-B. Ann Neurol. 2004;55:306–319. - PubMed
-
- Rowe C, Ng S, Ackermann U, Gong S, Pike K, Savage G, et al. Imaging beta-amyloid burden in aging and dementia. Neurology. 2007;68:1718–1725. - PubMed
-
- Nordberg A. Amyloid imaging in Alzheimer's disease. Curr Opin Neurol. 2007;20:398–402. - PubMed
-
- Price JC, Klunk WE, Lopresti BJ, Lu X, Hoge JA, Ziolko SK, et al. Kinetic modeling of amyloid binding in humans using PET imaging and Pittsburgh compound-B. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2005;25:1528–1547. - PubMed
-
- Lopresti BJ, Klunk WE, Mathis Ca, Hoge Ja, Ziolko SK, Lu X, et al. Simplified quantification of Pittsburgh compound B amyloid imaging PET studies: a comparative analysis. J Nucl Med. 2005;46:1959–1972. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

