Comparative effectiveness of fecal immunochemical test outreach, colonoscopy outreach, and usual care for boosting colorectal cancer screening among the underserved: a randomized clinical trial
- PMID: 23921906
- PMCID: PMC5228201
- DOI: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2013.9294
Comparative effectiveness of fecal immunochemical test outreach, colonoscopy outreach, and usual care for boosting colorectal cancer screening among the underserved: a randomized clinical trial
Abstract
Importance: Colorectal cancer (CRC) screening saves lives, but participation rates are low among underserved populations. Knowledge on effective approaches for screening the underserved, including best test type to offer, is limited.
Objective: To determine (1) if organized mailed outreach boosts CRC screening compared with usual care and (2) if FIT is superior to colonoscopy outreach for CRC screening participation in an underserved population.
Design, setting, and participants: We identified uninsured patients, not up to date with CRC screening, age 54 to 64 years, served by the John Peter Smith Health Network, Fort Worth and Tarrant County, Texas, a safety net health system.
Interventions: Patients were assigned randomly to 1 of 3 groups. One group was assigned to fecal immunochemical test (FIT) outreach, consisting of mailed invitation to use and return an enclosed no-cost FIT (n = 1593). A second was assigned to colonoscopy outreach, consisting of mailed invitation to schedule a no-cost colonoscopy (n = 479). The third group was assigned to usual care, consisting of opportunistic primary care visit–based screening (n = 3898). In addition, FIT and colonoscopy outreach groups received telephone follow-up to promote test completion.
Main outcome measures: Screening participation in any CRC test within 1 year after randomization.
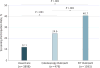
Results: Mean patient age was 59 years; 64% of patients were women. The sample was 41% white, 24% black, 29% Hispanic, and 7% other race/ethnicity. Screening participation was significantly higher for both FIT (40.7%) and colonoscopy outreach (24.6%) than for usual care (12.1%) (P < .001 for both comparisons with usual care). Screening was significantly higher for FIT than for colonoscopy outreach (P < .001). In stratified analyses, screening was higher for FIT and colonoscopy outreach than for usual care, and higher for FIT than for colonoscopy outreach among whites, blacks, and Hispanics (P < .005 for all comparisons). Rates of CRC identification and advanced adenoma detection were 0.4% and 0.8% for FIT outreach, 0.4% and 1.3% for colonoscopy outreach, and 0.2% and 0.4% for usual care, respectively (P < .05 for colonoscopy vs usual care advanced adenoma comparison; P > .05 for all other comparisons). Eleven of 60 patients with abnormal FIT results did not complete colonoscopy. CONCLUSIONS AND REVELANCE: Among underserved patients whose CRC screening was not up to date, mailed outreach invitations resulted in markedly higher CRC screening compared with usual care. Outreach was more effective with FIT than with colonoscopy invitation.
Trial registration: clinicaltrials.gov Identifier: NCT01191411.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: None reported.
Figures

Comment in
-
Dedicated outreach is effective in increasing uptake of colorectal cancer screening in an underserved population.Gastroenterology. 2014 Feb;146(2):577-9. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2013.12.011. Epub 2013 Dec 17. Gastroenterology. 2014. PMID: 24355612 No abstract available.
-
Mailed invitations for colorectal screening are effective in increasing screening participation in uninsured adults with faecal immunochemical testing: the preferred screening modality.Evid Based Med. 2014 Aug;19(4):145. doi: 10.1136/eb-2014-101772. Epub 2014 Apr 12. Evid Based Med. 2014. PMID: 24727711 No abstract available.
References
-
- US Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for colorectal cancer: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Ann Intern Med. 2008;149(9):627–637. - PubMed
-
- Levin B, Lieberman DA, McFarland B, et al. American Cancer Society Colorectal Cancer Advisory Group; US Multi-Society Task Force; American College of Radiology Colon Cancer Committee Screening and surveillance for the early detection of colorectal cancer and adenomatous polyps, 2008: a joint guideline from the American Cancer Society, the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer, and the American College of Radiology. Gastroenterology. 2008;134(5):1570–1595. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

