Kappa opioid receptors on dopaminergic neurons are necessary for kappa-mediated place aversion
- PMID: 23921954
- PMCID: PMC3828533
- DOI: 10.1038/npp.2013.171
Kappa opioid receptors on dopaminergic neurons are necessary for kappa-mediated place aversion
Abstract
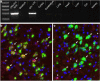
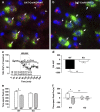
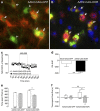
Kappa-opioid receptor (KOR) agonists have dysphoric properties in humans and are aversive in rodents. This has been attributed to the activation of KORs within the mesolimbic dopamine (DA) system. However, the role of DA in KOR-mediated aversion and stress remains divisive as recent studies have suggested that activation of KORs on serotonergic neurons may be sufficient to mediate aversive behaviors. To address this question, we used conditional knock-out (KO) mice with KORs deleted on DA neurons (DAT(Cre/wt)/KOR(loxp/loxp), or DATCre-KOR KO). In agreement with previous findings, control mice (DAT(Cre/wt)/KOR(wt/wt) or WT) showed conditioned place aversion (CPA) to the systemically administered KOR agonist U69,593. In contrast, DATCre-KOR KO mice did not exhibit CPA with this same agonist. In addition, in vivo microdialysis showed that systemic U69,593 decreased overflow of DA in the nucleus accumbens (NAc) in WT mice, but had no effect in DATCre-KOR KO mice. Intra- ventral tegmental area (VTA) delivery of KORs using an adeno-associated viral gene construct, resulted in phenotypic rescue of the KOR-mediated NAc DA response and aversive behavior in DATCre-KOR KO animals. These results provide evidence that KORs on VTA DA neurons are necessary to mediate KOR-mediated aversive behavior. Therefore, our data, along with recent findings, suggest that the neuronal mechanisms of KOR-mediated aversive behavior may include both dopaminergic and serotonergic components.
Figures
References
-
- Backman CM, Malik N, Zhang Y, Shan L, Grinberg A, Hoffer BJ, et al. Characterization of a mouse strain expressing Cre recombinase from the 3' untranslated region of the dopamine transporter locus. Genesis. 2006;44:383–390. - PubMed
-
- Bals-Kubik R, Ableitner A, Herz A, Shippenberg TS. Neuroanatomical sites mediating the motivational effects of opioids as mapped by the conditioned place preference paradigm in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993a;264:489–495. - PubMed
-
- Bals-Kubik R, Ableitner A, Herz A, Shippenberg TS. Neuroanatomical sites mediating the motivational effects of opioids as mapped by the conditioned place preference paradigm in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993b;264:489–495. - PubMed
-
- Carlezon WA, Jr, Beguin C, Dinieri JA, Baumann MH, Richards MR, Todtenkopf MS, et al. Depressive-like effects of the {kappa}-opioid receptor agonist salvinorin A on behavior and neurochemistry in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006;316:440–447. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

