RelB: an outlier in leukocyte biology
- PMID: 23922380
- PMCID: PMC3800064
- DOI: 10.1189/jlb.0513305
RelB: an outlier in leukocyte biology
Abstract
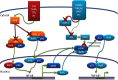
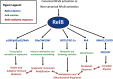
RelB is one of the more unusual members of the NF-κB family. This family, arguably the best known group of transcription regulators, regulates an astonishing array of cell types and biological processes. This includes regulation of cell growth, differentiation and death by apoptosis, and the development and function of the innate and adaptive-immune system. RelB is best known for its roles in lymphoid development, DC biology, and noncanonical signaling. Within the last few years, however, surprising functions of RelB have emerged. The N-terminal leucine zipper motif of RelB, a motif unique among the NF-κB family, may associate with more diverse DNA sequences than other NF-κB members. RelB is capable of direct binding to the AhR that supports the xenobiotic-detoxifying pathway. RelB can regulate the circadian rhythm by directly binding to the BMAL partner of CLOCK. Finally, RelB also couples with bioenergy NAD(+) sensor SIRT1 to integrate acute inflammation with changes in metabolism and mitochondrial bioenergetics. In this review, we will explore these unique aspects of RelB, specifically with regard to its role in immunity.
Keywords: NF-κB; bioenergy; endotoxin tolerance; inflammation.
Figures

References
-
- Hayden M. S. (2012) A less-canonical, canonical NF-κB pathway in DCs. Nat. Immunol. 13, 1139–1141 - PubMed
-
- Vallabhapurapu S., Karin M. (2009) Regulation and function of NF-κB transcription factors in the immune system. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 27, 693–733 - PubMed
-
- Yoza B. K., Hu J. Y., Cousart S. L., Forrest L. M., McCall C. E. (2006) Induction of RelB participates in endotoxin tolerance. J. Immunol. 177, 4080–4085 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

