Sealing Ability of Orthograde MTA and CEM Cement in Apically Resected Roots Using Bacterial Leakage Method
- PMID: 23922571
- PMCID: PMC3734512
Sealing Ability of Orthograde MTA and CEM Cement in Apically Resected Roots Using Bacterial Leakage Method
Abstract
Introduction: The aim of this in vitro study was to determine the sealing ability of orthograde ProRoot mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) and calcium enriched mixture (CEM) cement as root-end filling materials.
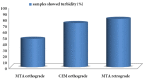
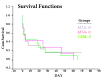
Materials and methods: Fifty four extracted single-rooted human teeth were used. The samples were randomly divided into 3 experimental groups. In group A and B, 4 mm of WMTA and CEM cement were placed in an orthograde manner and 3 mm of apices were resected after 24 hours. In group C the apical 3 mm of each root was resected and the root-end prepared with ultrasonic tips to a depth of 3 mm and subsequently, then filled with MTA. The apical sealing ability was performed with bacterial leakage method. Statistical analysis was carried out with Chi-square test.
Results: There were no significant differences in the extent of bacterial leakage between the three experimental groups (P>0.05).
Conclusion: Based on the limitations of this in vitro study, we concluded that MTA and CEM cement can be placed in an orthograde manner when there is a potential need for root-end surgery.
Keywords: Apicoectomy; Bacterial Leakage; CEM cement; Calcium Enriched Mixture; Mineral Trioxide Aggregate; Retrograde Obturation; Root Canal Filling Materials; Seal.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Kakehashi S, Stanley HR, Fitzgerald RJ. The Effects of Surgical Exposures of Dental Pulps in Germ-Free and Conventional Laboratory Rats. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1965;20:340–9. - PubMed
-
- Moller AJ, Fabricius L, Dahlen G, Ohman AE, Heyden G. Influence on periapical tissues of indigenous oral bacteria and necrotic pulp tissue in monkeys. Scand J Dent Res. 1981;89(6):475–84. - PubMed
-
- Montellano AM, Schwartz SA, Beeson TJ. Contamination of tooth-colored mineral trioxide aggregate used as a root-end filling material: a bacterial leakage study. J Endod. 2006;32(5):452–5. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources