A metabolically-stabilized phosphonate analog of lysophosphatidic acid attenuates collagen-induced arthritis
- PMID: 23923032
- PMCID: PMC3726599
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0070941
A metabolically-stabilized phosphonate analog of lysophosphatidic acid attenuates collagen-induced arthritis
Abstract
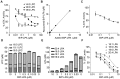
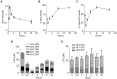
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a destructive arthropathy with systemic manifestations, characterized by chronic synovial inflammation. Under the influence of the pro-inflammatory milieu synovial fibroblasts (SFs), the main effector cells in disease pathogenesis become activated and hyperplastic while releasing a number of signals that include pro-inflammatory factors and tissue remodeling enzymes. Activated RA SFs in mouse or human arthritic joints express significant quantities of autotaxin (ATX), a lysophospholipase D responsible for the majority of lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) production in the serum and inflamed sites. Conditional genetic ablation of ATX from SFs resulted in attenuation of disease symptoms in animal models, an effect attributed to diminished LPA signaling in the synovium, shown to activate SF effector functions. Here we show that administration of 1-bromo-3(S)-hydroxy-4-(palmitoyloxy)butyl-phosphonate (BrP-LPA), a metabolically stabilized analog of LPA and a dual function inhibitor of ATX and pan-antagonist of LPA receptors, attenuates collagen induced arthritis (CIA) development, thus validating the ATX/LPA axis as a novel therapeutic target in RA.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Autotaxin expression from synovial fibroblasts is essential for the pathogenesis of modeled arthritis.J Exp Med. 2012 May 7;209(5):925-33. doi: 10.1084/jem.20112012. Epub 2012 Apr 9. J Exp Med. 2012. PMID: 22493518 Free PMC article.
-
The autotaxin-lysophosphatidic acid pathway in pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis.Eur J Pharmacol. 2015 Oct 15;765:228-33. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.08.028. Epub 2015 Aug 20. Eur J Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26297977 Review.
-
Osteoclast-Derived Autotaxin, a Distinguishing Factor for Inflammatory Bone Loss.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019 Nov;71(11):1801-1811. doi: 10.1002/art.41005. Epub 2019 Sep 30. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019. PMID: 31162832 Free PMC article.
-
[Function and biological activities of the autotaxin-LPA axis].Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2011 Dec 25;63(6):601-10. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2011. PMID: 22193457 Review. Chinese.
-
Necessity of lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1 for development of arthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 2013 Aug;65(8):2037-47. doi: 10.1002/art.37991. Arthritis Rheum. 2013. PMID: 23666827
Cited by
-
Regulation of T cell motility in vitro and in vivo by LPA and LPA2.PLoS One. 2014 Jul 8;9(7):e101655. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0101655. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25003200 Free PMC article.
-
The Bulk of Autotaxin Activity Is Dispensable for Adult Mouse Life.PLoS One. 2015 Nov 16;10(11):e0143083. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0143083. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26569406 Free PMC article.
-
The autotaxin-LPA axis emerges as a novel regulator of lymphocyte homing and inflammation.J Immunol. 2014 Feb 1;192(3):851-7. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1302831. J Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24443508 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Autotaxin-Lysophosphatidic Acid: From Inflammation to Cancer Development.Mediators Inflamm. 2017;2017:9173090. doi: 10.1155/2017/9173090. Epub 2017 Dec 21. Mediators Inflamm. 2017. PMID: 29430083 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Design and Development of Autotaxin Inhibitors.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021 Nov 22;14(11):1203. doi: 10.3390/ph14111203. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34832985 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- McInnes IB, Schett G (2011) The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med 365: 2205–2219. - PubMed
-
- Scott DL, Wolfe F, Huizinga TW (2010) Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 376: 1094–1108. - PubMed
-
- Strand V, Kimberly R, Isaacs JD (2007) Biologic therapies in rheumatology: lessons learned, future directions. Nat Rev Drug Discov 6: 75–92. - PubMed
-
- van Vollenhoven RF (2009) Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: state of the art 2009. Nat Rev Rheumatol 5: 531–541. - PubMed
-
- McInnes IB, Schett G (2007) Cytokines in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Immunol 7: 429–442. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

