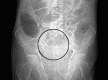
Self-expanding metallic stents for palliation and as a bridge to minimally invasive surgery in colorectal obstruction
- PMID: 23925013
- PMCID: PMC3771786
- DOI: 10.4293/108680813X13654754534990
Self-expanding metallic stents for palliation and as a bridge to minimally invasive surgery in colorectal obstruction
Abstract
Background and objectives: Acute colorectal obstruction is a potentially life-threatening emergency that requires immediate surgical treatment. Emergency procedures had an associated mortality rate of 10% to 30%. This encouraged development of other options, most notably self-expanding metallic stents. The primary endpoint of this study to is to report our group's experience.
Methods: We performed a retrospective review of 37 patients who underwent self-expanding metallic stent placement for colorectal obstruction between July 2000 and May 2012. Data collected were age, comorbidities, diagnosis, intent of intervention (palliative vs bridge to surgery), complications, and follow-up.
Results: The study comprised 21 men (56.76%) and 16 women (43.24%), with a mean age of 67 years. The intent of the procedure was definitive treatment in 22 patients (59.46%) and bridge to surgery in 15 (40.54%). The highest technical success rate was at the rectosigmoid junction (100%). The causes of technical failure were inability of the guidewire to traverse the stricture and bowel perforation related to stenting. The mean follow-up period was 9.67 months. Pain and constipation were the most common postprocedure complications.
Discussion: The use of a self-expanding metallic stent has been shown to be effective for palliation of malignant obstruction. It is associated with a lower incidence of intensive care unit admission, shorter hospital stay, lower stoma rate, and earlier chemotherapy administration. Laparoscopic or robotic surgery can then be performed in an elective setting on a prepared bowel. Therefore the patient benefits from advantages of the combination of 2 minimally invasive procedures in a nonemergent situation. Further large-scale prospective studies are necessary.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: Drs. Plasencia and Lujan are consultants for Ethicon Endo-Surgery.
Figures
References
-
- American Cancer Society Colorectal cancer. Available at: http://www.cancer.org/Cancer/ColonandRectumCancer/DetailedGuide/colorect... Accessed May 15, 2012
-
- Fischer A, Schrag H, Goos M, Obermaier R, Hopt U, Baier P. Transanal endoscopic tube decompression of acute colonic obstruction: experience with 51 cases. Surg Endosc. 2007;22(3):683–688 - PubMed
-
- Pirlet IA, Slim K, Kwiatkowski F, Michot F, Millat BL. Emergency preoperative stenting versus surgery for acute left-sided malignant colonic obstruction: a multicenter randomized controlled trial. Surg Endosc. 2010;25(6):1814–1821 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical