Age-dependent hepatic lymphoid organization directs successful immunity to hepatitis B
- PMID: 23925290
- PMCID: PMC3754256
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI68182
Age-dependent hepatic lymphoid organization directs successful immunity to hepatitis B
Abstract
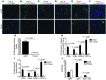
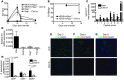
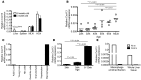
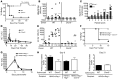
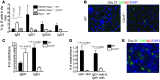
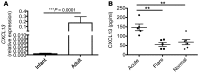
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a major human pathogen that causes immune-mediated hepatitis. Successful immunity to HBV is age dependent: viral clearance occurs in most adults, whereas neonates and young children usually develop chronic infection. Using a mouse model of HBV infection, we sought mechanisms underpinning the age-dependent outcome of HBV and demonstrated that hepatic macrophages facilitate lymphoid organization and immune priming within the adult liver and promote successful immunity. In contrast, lymphoid organization and immune priming was greatly diminished in the livers of young mice, and of macrophage-depleted adult mice, leading to abrogated HBV immunity. Furthermore, we found that CXCL13, which is involved in B lymphocyte trafficking and lymphoid architecture and development, is expressed in an age-dependent manner in both adult mouse and human hepatic macrophages and plays an integral role in facilitating an effective immune response against HBV. Taken together, these results identify some of the immunological mechanisms necessary for effective control of HBV.
Figures

Comment in
-
Antiviral immunity: A 'mature' way of controlling HBV.Nat Rev Immunol. 2013 Sep;13(9):616. doi: 10.1038/nri3527. Epub 2013 Aug 19. Nat Rev Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23954937 No abstract available.
References
-
- Robinson WS. Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 4th ed. London, United Kingdom: Churchill Livingstone; 1995.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P30DK026743/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01AI068090/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK063720/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI068090/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK026743/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- T32 AI007641/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI091872/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK093646/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R56AI091872/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK093646-02/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK060414/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

