Coordinating cell polarity and cell cycle progression: what can we learn from flies and worms?
- PMID: 23926048
- PMCID: PMC3758543
- DOI: 10.1098/rsob.130083
Coordinating cell polarity and cell cycle progression: what can we learn from flies and worms?
Abstract
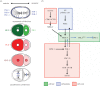
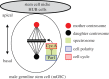
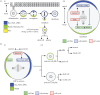
Spatio-temporal coordination of events during cell division is crucial for animal development. In recent years, emerging data have strengthened the notion that tight coupling of cell cycle progression and cell polarity in dividing cells is crucial for asymmetric cell division and ultimately for metazoan development. Although it is acknowledged that such coupling exists, the molecular mechanisms linking the cell cycle and cell polarity machineries are still under investigation. Key cell cycle regulators control cell polarity, and thus influence cell fate determination and/or differentiation, whereas some factors involved in cell polarity regulate cell cycle timing and proliferation potential. The scope of this review is to discuss the data linking cell polarity and cell cycle progression, and the importance of such coupling for asymmetric cell division. Because studies in model organisms such as Caenorhabditis elegans and Drosophila melanogaster have started to reveal the molecular mechanisms of this coordination, we will concentrate on these two systems. We review examples of molecular mechanisms suggesting a coupling between cell polarity and cell cycle progression.
Keywords: Caenorhabditis elegans; Drosophila melanogaster; cell cycle; cell polarity.
Figures


Similar articles
-
SPAT-1/Bora acts with Polo-like kinase 1 to regulate PAR polarity and cell cycle progression.Development. 2010 Oct;137(19):3315-25. doi: 10.1242/dev.055293. Development. 2010. PMID: 20823068
-
C. elegans Brat homologs regulate PAR protein-dependent polarity and asymmetric cell division.Dev Biol. 2008 Sep 15;321(2):368-78. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2008.06.037. Epub 2008 Jul 4. Dev Biol. 2008. PMID: 18652816
-
Mechanisms of asymmetric cell division: flies and worms pave the way.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008 May;9(5):355-66. doi: 10.1038/nrm2388. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18431399 Review.
-
Cell polarity and asymmetric cell division: the C. elegans early embryo.Essays Biochem. 2012;53:1-14. doi: 10.1042/bse0530001. Essays Biochem. 2012. PMID: 22928504 Review.
-
Meru co-ordinates spindle orientation with cell polarity and cell cycle progression.EMBO J. 2025 May;44(10):2949-2975. doi: 10.1038/s44318-025-00420-5. Epub 2025 Apr 1. EMBO J. 2025. PMID: 40169811 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Cell cycle expression of polarity genes features Rb targeting of Vang.Cells Dev. 2022 Mar;169:203747. doi: 10.1016/j.cdev.2021.203747. Epub 2021 Sep 25. Cells Dev. 2022. PMID: 34583062 Free PMC article.
-
Caenorhabditis elegans polo-like kinase PLK-1 is required for merging parental genomes into a single nucleus.Mol Biol Cell. 2015 Dec 15;26(25):4718-35. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E15-04-0244. Epub 2015 Oct 21. Mol Biol Cell. 2015. PMID: 26490119 Free PMC article.
-
Overcoming Clinical Resistance to EZH2 Inhibition Using Rational Epigenetic Combination Therapy.Cancer Discov. 2024 Jun 3;14(6):965-981. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-23-0110. Cancer Discov. 2024. PMID: 38315003 Free PMC article.
-
Protein polarization: Spatiotemporal precisions in cell division and differentiation.Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2022 Aug;68:102257. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2022.102257. Epub 2022 Jul 8. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2022. PMID: 35816992 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systems-level quantification of division timing reveals a common genetic architecture controlling asynchrony and fate asymmetry.Mol Syst Biol. 2015 Jun 10;11(6):814. doi: 10.15252/msb.20145857. Mol Syst Biol. 2015. PMID: 26063786 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Knoblich JA. 2010. Asymmetric cell division: recent developments and their implications for tumour biology. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 11, 849–860 (doi:10.1038/nrm3010). - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gonczy P. 2008. Mechanisms of asymmetric cell division: flies and worms pave the way. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 9, 355–366 (doi:10.1038/nrm2388) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fisher D, Krasinska L, Coudreuse D, Novak B. 2012. Phosphorylation network dynamics in the control of cell cycle transitions. J. Cell Sci. 125, 4703–4711 (doi:10.1242/jcs.106351) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hoege C, Hyman AA. 2013. Principles of PAR polarity in Caenorhabditis elegans embryos. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 14, 315–322 (doi:10.1038/nrm3558) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Homem CC, Knoblich JA. 2012. Drosophila neuroblasts: a model for stem cell biology. Development 139, 4297–4310 (doi:10.1242/dev.080515) - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

