Coordinating cell polarity and cell cycle progression: what can we learn from flies and worms?
- PMID: 23926048
- PMCID: PMC3758543
- DOI: 10.1098/rsob.130083
Coordinating cell polarity and cell cycle progression: what can we learn from flies and worms?
Abstract
Spatio-temporal coordination of events during cell division is crucial for animal development. In recent years, emerging data have strengthened the notion that tight coupling of cell cycle progression and cell polarity in dividing cells is crucial for asymmetric cell division and ultimately for metazoan development. Although it is acknowledged that such coupling exists, the molecular mechanisms linking the cell cycle and cell polarity machineries are still under investigation. Key cell cycle regulators control cell polarity, and thus influence cell fate determination and/or differentiation, whereas some factors involved in cell polarity regulate cell cycle timing and proliferation potential. The scope of this review is to discuss the data linking cell polarity and cell cycle progression, and the importance of such coupling for asymmetric cell division. Because studies in model organisms such as Caenorhabditis elegans and Drosophila melanogaster have started to reveal the molecular mechanisms of this coordination, we will concentrate on these two systems. We review examples of molecular mechanisms suggesting a coupling between cell polarity and cell cycle progression.
Keywords: Caenorhabditis elegans; Drosophila melanogaster; cell cycle; cell polarity.
Figures

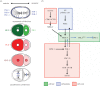
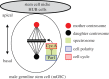
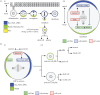

References
-
- Knoblich JA. 2010. Asymmetric cell division: recent developments and their implications for tumour biology. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 11, 849–860 (doi:10.1038/nrm3010). - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gonczy P. 2008. Mechanisms of asymmetric cell division: flies and worms pave the way. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 9, 355–366 (doi:10.1038/nrm2388) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fisher D, Krasinska L, Coudreuse D, Novak B. 2012. Phosphorylation network dynamics in the control of cell cycle transitions. J. Cell Sci. 125, 4703–4711 (doi:10.1242/jcs.106351) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hoege C, Hyman AA. 2013. Principles of PAR polarity in Caenorhabditis elegans embryos. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 14, 315–322 (doi:10.1038/nrm3558) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Homem CC, Knoblich JA. 2012. Drosophila neuroblasts: a model for stem cell biology. Development 139, 4297–4310 (doi:10.1242/dev.080515) - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
