Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, hepatic insulin resistance, and type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 23929732
- PMCID: PMC3946772
- DOI: 10.1002/hep.26672
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, hepatic insulin resistance, and type 2 diabetes
Abstract
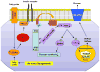
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), hepatic insulin resistance, and type 2 diabetes are all strongly associated and are all reaching epidemic proportions. Whether there is a causal link between NAFLD and hepatic insulin resistance is controversial. This review will discuss recent studies in both humans and animal models of NAFLD that have implicated increases in hepatic diacylglycerol (DAG) content leading to activation of novel protein kinase Cϵ (PKCϵ) resulting in decreased insulin signaling in the pathogenesis of NAFLD-associated hepatic insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. The DAG-PKCϵ hypothesis can explain the occurrence of hepatic insulin resistance observed in most cases of NAFLD associated with obesity, lipodystrophy, and type 2 diabetes.
© 2013 by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to disclose
Figures

References
-
- WHO. Obesity and Overweight Fact sheet N°311. 2012.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
