Dual Effects of Bilirubin on the Proliferation of Rat Renal NRK52E Cells and ITS Association with Gap Junctions
- PMID: 23930103
- PMCID: PMC3682199
- DOI: 10.2203/dose-response.12-003.Hei
Dual Effects of Bilirubin on the Proliferation of Rat Renal NRK52E Cells and ITS Association with Gap Junctions
Abstract
Objective: The effect of bilirubin on renal pathophysiology is controversial. This study aimed to observe the effects of bilirubin on the proliferation of normal rat renal tubular epithelial cell line (NRK52E) and its potential interplay with gap junction function.
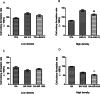
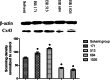
Methods: Cultured NRK52E cells, seeded respectively at high- or low- densities, were treated with varying concentrations of bilirubin for 24 hours. Cell injury was assessed by measuring cell viability and proliferation, and gap junction function was assessed by Parachute dye-coupling assay. Connexin 43 protein was assessed by Western blotting.
Results: At doses from 17.1 to 513μmol/L, bilirubin dose-dependently enhanced cell viability and colony-formation rates when cells were seeded at either high- or low- densities (all p<0.05 vs. solvent group) accompanied with enhanced intercellular fluorescence transmission and increased Cx43 protein expression in high-density cells. However, the above effects of BR were gradually reversed when its concentration increased from 684 to 1026μmol/L. In high-density cells, gap junction inhibitor 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate attenuated bilirubin-induced enhancement of colony-formation and fluorescence transmission. However, in the presence of high concentration bilirubin (1026μmol/L), activation of gap junction with retinoid acid decreased colony-formation rates.
Conclusion: Bilirubin can confer biphasic effects on renal NRK52E cell proliferation potentially by differentially affecting gap junction functions.
Keywords: Bilirubin; NRK52E cells; cell proliferation; connexin; gap junction; kidney injury.
Figures




References
-
- Adin CA, Croker BP, Agarwal A. Protective effects of exogenous bilirubin on ischemia-reperfusion injury in the isolated, perfused rat kidney. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2005;288:F778–84. - PubMed
-
- Alexandra Brito M, Silva RF, Brites D. Bilirubin toxicity to human erythrocytes: a review. Clin Chim Acta. 2006;374:46–56. - PubMed
-
- Alvares-da-Silva MR, Waechter FL, Francisconi CF, Barros E, Thomé F, Traiber C, Fonseca DL, Zingani JM, Sampaio JA, Pinto RD, Pereira-Lima L. Risk factors for postoperative acute renal failure at a new orthotopic liver transplantation program. Transplant. Proc. 1999;31:3050–3052. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

