SAR Based Optimization of a 4-Quinoline Carboxylic Acid Analog with Potent Anti-Viral Activity
- PMID: 23930152
- PMCID: PMC3733392
- DOI: 10.1021/ml300464h
SAR Based Optimization of a 4-Quinoline Carboxylic Acid Analog with Potent Anti-Viral Activity
Abstract
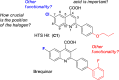
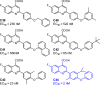
It is established that drugs targeting viral proteins are at risk of generating resistant strains. However, drugs targeting host factors can potentially avoid this problem. Herein we report structure-activity relationship studies leading to the discovery of a very potent lead compound 6-fluoro-2-(5-isopropyl-2-methyl-4-phenoxyphenyl)quinoline-4-carboxylic acid (C44) that inhibits human dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH) with an IC50 of 1 nM, and viral replication of VSV and WSN-Influenza with an EC50 of 2 nM and 41 nM. We also solved the X-ray structure of human DHODH bound to C44, providing structural insight into the potent inhibition of biaryl ether analogs of brequinar.
Keywords: anti-viral; high-throughput screening; human DHODH inhibitor; structure-activity relationship.
Figures


References
-
- De Clercq E., Ed. Antiviral Drug Strategies, 1st ed.; Wiley-VCH Verlag GMBH & Co KGaA: Berlin, Germany, 2011; Chapter 1.
-
- Richman D. D. The implications of drug resistance for strategies of combination antiviral chemotherapy. Antiviral Res. 1996, 29, 31–33. - PubMed
-
- Katze M. G.; He Y.; Michael G. Jr. Viruses and interferon: a fight for supremacy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 2, 675–687. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

