Cellular resolution models for even skipped regulation in the entire Drosophila embryo
- PMID: 23930223
- PMCID: PMC3736529
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.00522
Cellular resolution models for even skipped regulation in the entire Drosophila embryo
Abstract
Transcriptional control ensures genes are expressed in the right amounts at the correct times and locations. Understanding quantitatively how regulatory systems convert input signals to appropriate outputs remains a challenge. For the first time, we successfully model even skipped (eve) stripes 2 and 3+7 across the entire fly embryo at cellular resolution. A straightforward statistical relationship explains how transcription factor (TF) concentrations define eve's complex spatial expression, without the need for pairwise interactions or cross-regulatory dynamics. Simulating thousands of TF combinations, we recover known regulators and suggest new candidates. Finally, we accurately predict the intricate effects of perturbations including TF mutations and misexpression. Our approach imposes minimal assumptions about regulatory function; instead we infer underlying mechanisms from models that best fit the data, like the lack of TF-specific thresholds and the positional value of homotypic interactions. Our study provides a general and quantitative method for elucidating the regulation of diverse biological systems. DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.00522.001.
Keywords: D. melanogaster; developmental patterning; even skipped; fly embryo; logistic regression; positional information; transcriptional regulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures
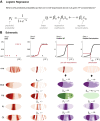
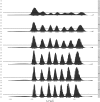
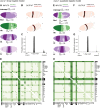
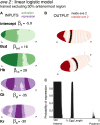
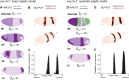
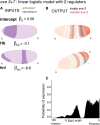
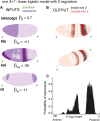
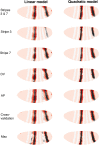


Comment in
-
Computing away the magic?Elife. 2013 Aug 6;2:e01135. doi: 10.7554/eLife.01135. Elife. 2013. PMID: 23930226 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Computing away the magic?Elife. 2013 Aug 6;2:e01135. doi: 10.7554/eLife.01135. Elife. 2013. PMID: 23930226 Free PMC article.
-
Natural variation of the expression pattern of the segmentation gene even-skipped in melanogaster.Dev Biol. 2015 Sep 1;405(1):173-81. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2015.06.019. Epub 2015 Jun 27. Dev Biol. 2015. PMID: 26129990 Free PMC article.
-
The dynamic transmission of positional information in stau- mutants during Drosophila embryogenesis.Elife. 2020 Jun 8;9:e54276. doi: 10.7554/eLife.54276. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32511091 Free PMC article.
-
Drosophila blastoderm patterning.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2012 Dec;22(6):533-41. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2012.10.005. Epub 2013 Jan 4. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2012. PMID: 23290311 Review.
-
Dynamic positional information: Patterning mechanism versus precision in gradient-driven systems.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2020;137:219-246. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctdb.2019.11.017. Epub 2019 Dec 24. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32143744 Review.
Cited by
-
Inferring regulatory networks from experimental morphological phenotypes: a computational method reverse-engineers planarian regeneration.PLoS Comput Biol. 2015 Jun 4;11(6):e1004295. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004295. eCollection 2015 Jun. PLoS Comput Biol. 2015. PMID: 26042810 Free PMC article.
-
Fully interpretable deep learning model of transcriptional control.Bioinformatics. 2020 Jul 1;36(Suppl_1):i499-i507. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btaa506. Bioinformatics. 2020. PMID: 32657418 Free PMC article.
-
Shadow enhancers enable Hunchback bifunctionality in the Drosophila embryo.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Jan 20;112(3):785-90. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1413877112. Epub 2015 Jan 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25564665 Free PMC article.
-
Ancestral resurrection of the Drosophila S2E enhancer reveals accessible evolutionary paths through compensatory change.Mol Biol Evol. 2014 Apr;31(4):903-16. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msu042. Epub 2014 Jan 9. Mol Biol Evol. 2014. PMID: 24408913 Free PMC article.
-
Multifaceted effects on even-skipped transcriptional dynamics upon Krüppel dosage changes.Development. 2024 Mar 1;151(5):dev202132. doi: 10.1242/dev.202132. Epub 2024 Mar 4. Development. 2024. PMID: 38345298 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andrioli LP, Vasisht V, Theodosopoulou E, Oberstein A, Small S. Anterior repression of a Drosophila stripe enhancer requires three position-specific mechanisms. Development. 2002;129:4931–40. http://dev.biologists.org/content/129/21/4931.long - PubMed
-
- Arnosti DN, Barolo S, Levine M, Small S. The eve stripe 2 enhancer employs multiple modes of transcriptional synergy. Development. 1996;122:205–14. http://dev.biologists.org/content/122/1/205.abstract - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

