An insight into genetics of non-syndromic cleft palate
- PMID: 23930251
- PMCID: PMC3732890
- DOI: 10.4103/2277-9175.107969
An insight into genetics of non-syndromic cleft palate
Abstract
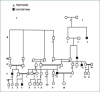
Our proband is a 29-year-old man, who is affected with soft cleft palate and hypernasality. A study of about six generations of this family pedigree shows that cleft palate has repeatedly occurred in males, with probably a X-linked recessive pattern of inheritance. Interestingly, the sister of the proband is affected with hypernasality and she has an affected son. This is the first report of X-linked inheritance pattern of cleft palate in Iran.
Keywords: Cleft palate; X-linked; inheritance pattern.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Moore G, Jvens A, Chambers J, Bjornsson A, Arnason A, Jensson O, et al. The application of molecular genetics to detection of craniofacial abnormality. Development. 1988;103(Suppl):233–9. - PubMed
-
- Bush JO, Lan Y, Maltby KM, Jiang R. Isolation and developmental expression analysis of Tbx22, the mouse homolog of the human X-linked cleft palate gene. Dev Dyn. 2002;225:322–6. - PubMed
-
- Cobourne MT. The complex genetics of cleft lip and palate. Eur J Orthod. 2004;26:7–16. - PubMed
-
- Fletcher SG. Contingencies for bio-electronic modification of nasality. J Speech Hear Disord. 1972;37:329–46. - PubMed
-
- Weiss CE. The speech pathologist's role in dealing with obturator-wearing school children. J Speech Hear Disord. 1974;39:155–62. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources