Newly developed strategies for improving sensitivity to radiation by targeting signal pathways in cancer therapy
- PMID: 23930697
- PMCID: PMC7654251
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.12252
Newly developed strategies for improving sensitivity to radiation by targeting signal pathways in cancer therapy
Abstract
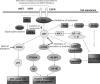
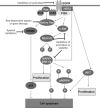
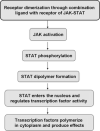
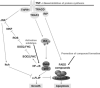
Inherent and acquired resistance of cancer cells is increasingly recognized as a significant impediment to effective radiation cancer treatment. As important intracellular factors, aberrant tumor transmembrane signal transduction pathways, which include the prosurvival cascades (PI3K/Akt, MAPK/ERK and JAK/STAT) and the proapoptosis pathways (Wnt, p53 and TNF-α/NF-κB), have been proved to be crucial determinants of the probability of cell sensitivity to radiation in malignant lesions. There is increasing evidence that targeting the abnormal pathways that can regulate the activity of the DNA damage response and further influence the response of tumor cells to radiation may be suitable for improving radiation sensitization. Preclinical and clinical evidence suggest that agents targeting aberrant tumor signals can effectively improve the therapeutic effect of ionizing radiation. Therefore, in this review, we discuss the intricate interplay between tumor responses to radiation with the aberrant signal pathways, and the potential druggable targets within the pathways to sensitize tumors without significant collateral damage to normal tissues. The application of novel targeting compounds to manipulate the aberrant signal of tumor cells in clinical treatments is also addressed.
© 2013 Japanese Cancer Association.
Figures
References
-
- Yorke E, Gelblum D, Ford E. Patient safety in external beam radiation therapy. Am J Roentgenol 2011; 196: 768–72. - PubMed
-
- Milosevic MF. Hypoxia, anerobic metabolism, and interstitial hypertension. In: Siemann DW, ed. Tumor Microenvironment, 1st edn. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons Ltd, 2010; 183–205.
-
- Wachsberger P, Burd R, Dicker AP. Tumor response to ionizing radiation combined with antiangiogenesis or vascular targeting agents: exploring mechanisms of interaction. Clin Cancer Res 2003; 9: 1957–71. - PubMed
-
- Kasten‐Pisula U, Menegakis A, Brammer I et al The extreme radiosensitivity of the squamous cell carcinoma SKX is due to a defect in double‐strand break repair. Radiother Oncol 2009; 90: 257–64. - PubMed
-
- Zhivotovsky B, Joseph B, Orrenius S. Tumor radiosensitivity and apoptosis. Exp Cell Res 1999; 248: 10–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

