Simultaneous digital quantification and fluorescence-based size characterization of massively parallel sequencing libraries
- PMID: 23931593
- PMCID: PMC4018218
- DOI: 10.2144/000114063
Simultaneous digital quantification and fluorescence-based size characterization of massively parallel sequencing libraries
Abstract
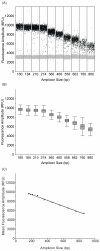
Due to the high cost of failed runs and suboptimal data yields, quantification and determination of fragment size range are crucial steps in the library preparation process for massively parallel sequencing (or next-generation sequencing). Current library quality control methods commonly involve quantification using real-time quantitative PCR and size determination using gel or capillary electrophoresis. These methods are laborious and subject to a number of significant limitations that can make library calibration unreliable. Herein, we propose and test an alternative method for quality control of sequencing libraries using droplet digital PCR (ddPCR). By exploiting a correlation we have discovered between droplet fluorescence and amplicon size, we achieve the joint quantification and size determination of target DNA with a single ddPCR assay. We demonstrate the accuracy and precision of applying this method to the preparation of sequencing libraries.
Figures



References
-
- Martin JA, Wang Z. Next-generation transcriptome assembly. Nature reviews. Genetics. 2011;12:671–682. - PubMed
-
- Voelkerding KV, Dames SA, Durtschi JD. Next-generation sequencing: from basic research to diagnostics. Clinical chemistry. 2009;55:641–658. - PubMed
-
- Su Z, Ning B, Fang H, Hong H, Perkins R, Tong W, Shi L. Next-generation sequencing and its applications in molecular diagnostics. Expert review of molecular diagnostics. 2011;11:333–343. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
