Candidate gene analysis of the surfactant protein D gene in pediatric diffuse lung disease
- PMID: 23932215
- PMCID: PMC3846094
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2013.06.063
Candidate gene analysis of the surfactant protein D gene in pediatric diffuse lung disease
Abstract
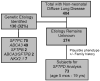
Mutations in surfactant-associated genes cause childhood diffuse lung disease. Mice lacking surfactant protein D develop lung disease with age. However, we identified no novel surfactant protein D gene (SFTPD) coding or splice region variants in 73 unrelated children with diffuse lung disease from a cohort enriched for genetic surfactant dysfunction.
Keywords: DLD; Diffuse lung disease; SFTPD; SNP; SP; Single nucleotide polymorphism; Surfactant protein; Surfactant protein D gene.
Copyright © 2013 Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Surfactant protein D is a candidate biomarker for subclinical tobacco smoke-induced lung damage.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2014 May 1;306(9):L887-95. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00340.2013. Epub 2014 Mar 7. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24610936
-
Correction of pulmonary abnormalities in Sftpd-/- mice requires the collagenous domain of surfactant protein D.J Biol Chem. 2006 Aug 25;281(34):24496-505. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M600651200. Epub 2006 Jun 20. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16787926
-
Polymorphisms in the human surfactant protein-D (SFTPD) gene: strong evidence that serum levels of surfactant protein-D (SP-D) are genetically influenced.Immunogenetics. 2005 Apr;57(1-2):1-7. doi: 10.1007/s00251-005-0775-5. Epub 2005 Feb 8. Immunogenetics. 2005. PMID: 15700120 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic variant associations of human SP-A and SP-D with acute and chronic lung injury.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2012 Jan 1;17(2):407-29. doi: 10.2741/3935. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2012. PMID: 22201752 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Surfactant protein A and surfactant protein D variation in pulmonary disease.Immunobiology. 2007;212(4-5):381-416. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2007.01.003. Epub 2007 Feb 23. Immunobiology. 2007. PMID: 17544823 Review.
Cited by
-
Surfactant Protein D in Respiratory and Non-Respiratory Diseases.Front Med (Lausanne). 2018 Feb 8;5:18. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2018.00018. eCollection 2018. Front Med (Lausanne). 2018. PMID: 29473039 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic causes of surfactant protein abnormalities.Curr Opin Pediatr. 2019 Jun;31(3):330-339. doi: 10.1097/MOP.0000000000000751. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2019. PMID: 31090574 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic Testing for Neonatal Respiratory Disease.Children (Basel). 2021 Mar 11;8(3):216. doi: 10.3390/children8030216. Children (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33799761 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The oncogenic landscape of the idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a narrative review.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2022 Mar;11(3):472-496. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-21-880. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35399571 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms Interactions of the Surfactant Protein Genes Associated With Respiratory Distress Syndrome Susceptibility in Preterm Infants.Front Pediatr. 2021 Oct 4;9:682160. doi: 10.3389/fped.2021.682160. eCollection 2021. Front Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 34671583 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Korfhagen TR, Sheftelyevich V, Burhans MS, Bruno MD, Ross GF, Wert SE, et al. Surfactant protein-D regulates surfactant phospholipid homeostasis in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:28438–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

