Myf5-positive satellite cells contribute to Pax7-dependent long-term maintenance of adult muscle stem cells
- PMID: 23933088
- PMCID: PMC4082715
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2013.07.016
Myf5-positive satellite cells contribute to Pax7-dependent long-term maintenance of adult muscle stem cells
Erratum in
- Cell Stem Cell. 2013 Dec 5;13(6):769
Abstract
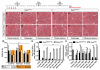
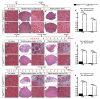
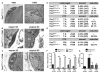
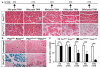
Skeletal muscle contains Pax7-expressing muscle stem or satellite cells, enabling muscle regeneration throughout most of adult life. Here, we demonstrate that induced inactivation of Pax7 in Pax7-expressing cells of adult mice leads to loss of muscle stem cells and reduced heterochromatin condensation in rare surviving satellite cells. Inactivation of Pax7 in Myf5-expressing cells revealed that the majority of adult muscle stem cells originate from myogenic lineages, which express the myogenic regulators Myf5 or MyoD. Likewise, the majority of muscle stem cells are replenished from Myf5-expressing myogenic cells during adult life, and inactivation of Pax7 in Myf5-expressing cells after muscle damage leads to a complete arrest of muscle regeneration. Finally, we demonstrate that a relatively small number of muscle stem cells are sufficient for efficient repair of skeletal muscles. We conclude that Pax7 acts at different levels in a nonhierarchical regulatory network controlling muscle-satellite-cell-mediated muscle regeneration.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Braun T, Gautel M. Transcriptional mechanisms regulating skeletal muscle differentiation, growth and homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2011;12:349–361. - PubMed
-
- Bulut-Karslioglu A, Perrera V, Scaranaro M, de la Rosa-Velazquez IA, van de Nobelen S, Shukeir N, Popow J, Gerle B, Opravil S, Pagani M, et al. A transcription factor-based mechanism for mouse heterochromatin formation. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2012;19:1023–1030. - PubMed
-
- Cooper RN, Tajbakhsh S, Mouly V, Cossu G, Buckingham M, Butler-Browne GS. In vivo satellite cell activation via Myf5 and MyoD in regenerating mouse skeletal muscle. J. Cell Sci. 1999;112:2895–2901. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

