Ribonucleotide reductase inhibitors hydroxyurea, didox, and trimidox inhibit human cytomegalovirus replication in vitro and synergize with ganciclovir
- PMID: 23933116
- PMCID: PMC3843955
- DOI: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2013.07.016
Ribonucleotide reductase inhibitors hydroxyurea, didox, and trimidox inhibit human cytomegalovirus replication in vitro and synergize with ganciclovir
Abstract
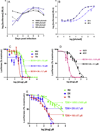
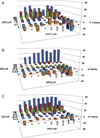
Ganciclovir (GCV) is a deoxyguanosine analog that is effective in inhibiting human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) replication. In infected cells GCV is converted to GCV-triphosphate which competes with dGTP for incorporation into the growing DNA strand by the viral DNA polymerase. Incorporated GCV promotes chain termination as it is an inefficient substrate for elongation. Because viral DNA synthesis also relies on cellular ribonucleotide reductase (RR) to synthesize deoxynucleotides, RR inhibitors are predicted to inhibit HCMV replication. Moreover, as dGTP competes with GCV-triphosphate for incorporation, RR inhibitors may also synergize with GCV by reducing intracellular dGTP levels and there by promoting increased GCV-triphosphate utilization by DNA polymerase. To investigate potential of RR inhibitors as anti-HCMV agents both alone and in combination with GCV, HCMV-inhibitory activities of three RR inhibitors, hydroxyurea, didox, and trimidox, were determined. In both spread inhibition and yield reduction assays RR inhibitors had modest anti-HCMV activity with 50% inhibitory concentrations ranging from 36±1.7 to 221±52μM. However, all three showed significant synergy with GCV at concentrations below their 50% inhibitory and 50% toxic concentrations. These results suggest that combining GCV with relatively low doses of RR inhibitors could significantly potentiate the anti-HCMV activity of GCV in vivo and could improve clinical response to therapy.
Keywords: Antivirals; Cytomegalovirus; Didox; Ganciclovir; Hydroxyurea; Trimidox.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Bernstein DI, Rheins LA. Solar simulator-induced herpes simplex labialis: use in evaluating treatment with acyclovir plus 348U87. Antiviral Res. 1994;23:225–233. - PubMed
-
- Boehmer PE, Lehman IR. Herpes simplex virus DNA replication. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1997;66:347–384. - PubMed
-
- Bridges CG, Ahmed SP, Sunkara PS, McCarthy JR, Tyms AS. The ribonucleotide reductase inhibitor (E)-2′-fluoromethylene-2′-deoxycytidine (MDL 101,731): a potential topical therapy for herpes simplex virus infection. Antiviral Res. 1995;27:325–334. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

