An unbiased peptide-wide discovery approach to select Mycobacterium tuberculosis antigens that target CD8+ T cell response during infection
- PMID: 23933335
- PMCID: PMC3778375
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2013.07.077
An unbiased peptide-wide discovery approach to select Mycobacterium tuberculosis antigens that target CD8+ T cell response during infection
Abstract
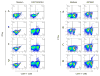
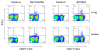
Accruing data strongly support the possible role of CD8+ T cells in immunity against tuberculosis (TB). Multivalent vaccines against Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) that incorporate CD8+ T cell antigens with those that elicit CD4+ T cells are therefore highly desirable. To screen for potential CD8+ T cell antigens that are produced by Mtb during infection, we isolated pathogen-derived peptides that bound to MHC Class I molecules expressed in adherent splenocytes obtained from Mtb-infected mice. Mass spectroscopy analysis revealed the following four nonamer peptides that had 100% homology with Mtb proteins: DGYVGAPAH (MT_0401), TTMPLFAD (MT_1164), RSGAATPVR (MT_2160.1) and LAAVVGVVL (MT_0078). The gene MT_0401 codes the protein 5'-phosphoribosylglycinamide transformylase 2 and the other three genes code for hypothetical proteins with unknown function. The NCBI/Blast analysis showed that among the four peptides DGYVGAPAH had the highest maximum alignment score and lowest E value (number of alignments expected by chance). Therefore, we assessed whether MT_0401 expressed in two genetic vaccine formulations was capable of stimulating CD8+ T cell response that is specific to DGYVGAPAH peptide. When mice were immunized with a recombinant plasmid DNA and an E1/E3-deleted Adenovirus 5 expressing MT0401 protein, using both homologous and heterologous prime-boost protocols, they developed strong DGYVGAPAH-specific CD8+ T cell response as well as antibody and CD4+ specific T cell response to the full length MT0401 protein. Equally important was the observation that mice infected with Mtb developed DGYVGAPAH-specific CD8+ T cell responses in both spleen and lungs. These results demonstrate that Mtb antigens that are processed and presented via MHC Class I machinery can be readily identified by the described approach and may be useful candidate antigens to stimulate specific CD8+ T cell responses in vaccine development programs.
Keywords: CD8 associated antigen; Immunogenicity; MT0401; Tuberculosis.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Global Tuberculosis Report. World Health Organization; 2012. WHO Report 2012.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

