Inhibitory effects of rosiglitazone on paraquat-induced acute lung injury in rats
- PMID: 23933652
- PMCID: PMC4002157
- DOI: 10.1038/aps.2013.65
Inhibitory effects of rosiglitazone on paraquat-induced acute lung injury in rats
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the effects of the PPAR-γ agonist rosiglitazone on acute lung injury induced by the herbicide paraquat (PQ) and the underlying mechanisms of action.
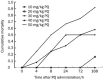
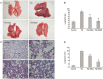
Methods: Male Sprague-Dawley rats were injected with PQ (20 mg/kg, ip). Rosiglitazone (3 or 10 mg/kg, ip) was administered 1 h before PQ exposure. Peripheral blood was collected at 4, 8, 24 and 72 h after PQ exposure for measuring the levels of MDA, TNF-α and IL-1β, and the SOD activity. Lung tissues were collected at 72 h after PQ exposure to determine the wet-to-dry (W/D) ratios and lung injury scores, as well as the protein levels of NF-κBp65, PPAR-γ, Nrf2, IκBα and pIκBα.
Results: At 72 h after PQ exposure, the untreated rats showed a 100% cumulative mortality, whereas no death was observed in rosiglitazone-pretreated rats. Moreover, rosiglitazone pretreatment dose-dependently attenuated PQ-induced lung edema and lung histopathological changes. The pretreatment significantly reduced the levels of TNF-α, IL-1β and MDA, increased SOD activity in the peripheral blood of PQ-treated rats. The pretreatment also efficiently activated PPAR-γ, induced Nrf2 expression and inhibited NF-κB activation in the lung tissues of PQ-treated rats. Furthermore, the pretreatment dose-dependently inhibited IκB-α degradation and phosphorylation, thus inhibiting NF-κB activation.
Conclusion: Pretreatment with rosiglitazone protects rats against PQ-induced acute lung injury by activating PPAR-γ, inducing Nrf2 expression and inhibiting NF-κB activation.
Figures



References
-
- Suntres ZE. Role of antioxidants in paraquat toxicity. Toxicology. 2002;180:65–77. - PubMed
-
- Parvez S, Raisuddin S. Effects of paraquat on the freshwater fish Channa punctata: non-enzymatic antioxidants as biomarkers of exposure. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol. 2006;50:392–7. - PubMed
-
- Neves FF, Sousa RB, Pazin-Filho A, Cupo P, Elias Júnior J, Nogueira-Barbosa MH. Severe paraquat poisoning: clinical and radiological findings in a survivor. J Bras Pneumol. 2010;36:513–6. - PubMed
-
- Venkatesan N. Pulmonary protective effects of curcumin against paraquat toxicity. Life Sci. 2000;66:21–8. - PubMed
-
- Yasaka T, Okudaira K, Fujito H, Matsumoto J, Ohya I, Miyamoto Y. Further studies of lipid peroxidation in human paraquat poisoning. Arch Intern Med. 1986;146:681–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

