Intracortical multiplication of thalamocortical signals in mouse auditory cortex
- PMID: 23933752
- PMCID: PMC3844430
- DOI: 10.1038/nn.3493
Intracortical multiplication of thalamocortical signals in mouse auditory cortex
Abstract
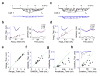
Cortical processing of sensory information begins with the transformation of thalamically relayed signals. We optogenetically silenced intracortical circuits to isolate thalamic inputs to layer 4 neurons and found that intracortical excitation linearly amplified thalamocortical responses underlying frequency and direction selectivity, with spectral range and tuning preserved, and prolonged the response duration. This signal pre-amplification and prolongation enhanced the salience of thalamocortically relayed information and ensured its robust, faithful and more persistent representation.
Figures

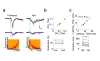
Comment in
-
A finely tuned cortical amplifier.Nat Neurosci. 2013 Sep;16(9):1166-8. doi: 10.1038/nn.3507. Nat Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23982448 No abstract available.
-
Intrinsic cortical signal gain: optogenetic silencing reveals active role of cortical amplification during sensory input.Neurosurgery. 2014 Feb;74(2):N22-3. doi: 10.1227/01.neu.0000442981.91829.01. Neurosurgery. 2014. PMID: 24435150 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

