FGF21 contributes to neuroendocrine control of female reproduction
- PMID: 23933983
- PMCID: PMC3769455
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.3250
FGF21 contributes to neuroendocrine control of female reproduction
Abstract
Preventing reproduction during nutritional deprivation is an adaptive process that is conserved and essential for the survival of species. In mammals, the mechanisms that inhibit fertility during starvation are complex and incompletely understood. Here we show that exposure of female mice to fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21), a fasting-induced hepatokine, mimics infertility secondary to starvation. Mechanistically, FGF21 acts on the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) in the hypothalamus to suppress the vasopressin-kisspeptin signaling cascade, thereby inhibiting the proestrus surge in luteinizing hormone. Mice lacking the FGF21 co-receptor, β-Klotho, in the SCN are refractory to the inhibitory effect of FGF21 on female fertility. Thus, FGF21 defines an important liver-neuroendocrine axis that modulates female reproduction in response to nutritional challenge.
Figures

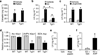
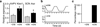
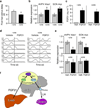
Comment in
-
Neuroendocrinology: Signalling starvation.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2013 Oct;14(10):670-1. doi: 10.1038/nrn3592. Epub 2013 Aug 29. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23985832 No abstract available.
References
-
- Burks DJ, et al. IRS-2 pathways integrate female reproduction and energy homeostasis. Nature. 2000;407:377–382. - PubMed
-
- Chehab FF, Lim ME, Lu R. Correction of the sterility defect in homozygous obese female mice by treatment with the human recombinant leptin. Nature Genetics. 1996;12:318–320. - PubMed
-
- Della Torre S, et al. Amino acid-dependent activation of liver estrogen receptor alpha integrates metabolic and reproductive functions via IGF-1. Cell Metabolism. 13:205–214. - PubMed
-
- Kalamatianos T, Grimshaw SE, Poorun R, Hahn JD, Coen CW. Fasting reduces KiSS-1 expression in the anteroventral periventricular nucleus (AVPV): effects of fasting on the expression of KiSS-1 and neuropeptide Y in the AVPV or arcuate nucleus of female rats. Journal of Neuroendocrinology. 2008;20:1089–1097. - PubMed
Online Methods References
-
- Casanova E, et al. A CamKIIalpha iCre BAC allows brain-specific gene inactivation. Genesis. 2001;31:37–42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R56DK089600/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007062/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- RL1GM084436/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- RL1 GM084436/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DK089600/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U19 DK062434/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HD028934/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U54-HD28934/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U19DK62434/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK067158/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- GM007062/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK067158/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

