The periplasmic HrpB1 protein from Xanthomonas spp. binds to peptidoglycan and to components of the type III secretion system
- PMID: 23934485
- PMCID: PMC3811196
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.01226-13
The periplasmic HrpB1 protein from Xanthomonas spp. binds to peptidoglycan and to components of the type III secretion system
Abstract
The plant-pathogenic bacterium Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria employs a type III secretion (T3S) system to translocate bacterial effector proteins into eukaryotic host cells. The membrane-spanning secretion apparatus consists of 11 core components and several associated proteins with yet unknown functions. In this study, we analyzed the role of HrpB1, which was previously shown to be essential for T3S and the formation of the extracellular T3S pilus. We provide experimental evidence that HrpB1 localizes to the bacterial periplasm and binds to peptidoglycan, which is in agreement with its predicted structural similarity to the putative peptidoglycan-binding domain of the lytic transglycosylase Slt70 from Escherichia coli. Interaction studies revealed that HrpB1 forms protein complexes and binds to T3S system components, including the inner membrane protein HrcD, the secretin HrcC, the pilus protein HrpE, and the putative inner rod protein HrpB2. The analysis of deletion and point mutant derivatives of HrpB1 led to the identification of amino acid residues that contribute to the interaction of HrpB1 with itself and HrcD and/or to protein function. The finding that HrpB1 and HrpB2 colocalize to the periplasm and both interact with HrcD suggests that they are part of a periplasmic substructure of the T3S system.
Figures
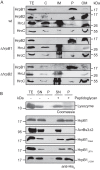

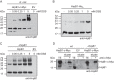


References
-
- Leyns F, De Cleene M, Swings J, De Ley J. 1984. The host range of the genus Xanthomonas. Bot. Rev. 50:305–355
-
- Chan JWYF, Goodwin PH. 1999. The molecular genetics of virulence of Xanthomonas campestris. Biotechnol. Adv. 17:489–508 - PubMed
-
- Francis MR, Sosinsky GE, Thomas D, DeRosier DJ. 1994. Isolation, characterization and structure of bacterial flagellar motors containing the switch complex. J. Mol. Biol. 235:1261–1270 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

