Development of a tunable wide-range gene induction system useful for the study of streptococcal toxin-antitoxin systems
- PMID: 23934493
- PMCID: PMC3811191
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.02320-13
Development of a tunable wide-range gene induction system useful for the study of streptococcal toxin-antitoxin systems
Abstract
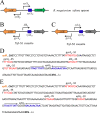
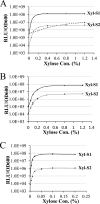
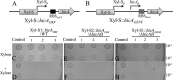
Despite the plethora of genetic tools that have been developed for use in Streptococcus mutans, the S. mutans genetic system still lacks an effective gene induction system exhibiting low basal expression and strong inducibility. Consequently, we created two hybrid gene induction cassettes referred to as Xyl-S1 and Xyl-S2. Both Xyl-S cassettes are xylose inducible and controlled by the Bacillus megaterium xylose repressor. The Xyl-S cassettes each demonstrated >600-fold-increased reporter activity in the presence of 1.2% (wt/vol) xylose. However, the Xyl-S1 cassette yielded a much higher maximum level of gene expression, whereas the Xyl-S2 cassette exhibited much lower uninduced basal expression. The cassettes also performed similarly in Streptococcus sanguinis and Streptococcus gordonii, which suggests that they are likely to be useful in a variety of streptococci. We demonstrate how both Xyl-S cassettes are particularly useful for the study of toxin-antitoxin (TA) modules using both the previously characterized S. mutans mazEF TA module and a previously uncharacterized HicAB TA module in S. mutans. HicAB TA modules are widely distributed among bacteria and archaea, but little is known about their function. We show that HicA serves as the toxin component of the module, while HicB serves as the antitoxin. Our results suggest that, in contrast to that of typical TA modules, HicA toxicity in S. mutans is modest at best. The implications of these results for HicAB function are discussed.
Figures

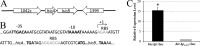
Similar articles
-
Characterization of HicAB toxin-antitoxin module of Sinorhizobium meliloti.BMC Microbiol. 2019 Jan 10;19(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s12866-018-1382-6. BMC Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30630415 Free PMC article.
-
The chromosomal mazEF locus of Streptococcus mutans encodes a functional type II toxin-antitoxin addiction system.J Bacteriol. 2011 Mar;193(5):1122-30. doi: 10.1128/JB.01114-10. Epub 2010 Dec 23. J Bacteriol. 2011. PMID: 21183668 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptation of Prokaryotic Toxins for Negative Selection and Cloning-Independent Markerless Mutagenesis in Streptococcus Species.mSphere. 2023 Jun 22;8(3):e0068222. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00682-22. Epub 2023 Apr 24. mSphere. 2023. PMID: 37093065 Free PMC article.
-
Structural overview of toxin-antitoxin systems in infectious bacteria: a target for developing antimicrobial agents.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Jun;1834(6):1155-67. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2013.02.027. Epub 2013 Feb 28. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23459128 Review.
-
Toxins, Targets, and Triggers: An Overview of Toxin-Antitoxin Biology.Mol Cell. 2018 Jun 7;70(5):768-784. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2018.01.003. Epub 2018 Feb 3. Mol Cell. 2018. PMID: 29398446 Review.
Cited by
-
Fine-tuned production of hydrogen peroxide promotes biofilm formation of Streptococcus parasanguinis by a pathogenic cohabitant Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans.Environ Microbiol. 2016 Nov;18(11):4023-4036. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.13425. Epub 2016 Jul 22. Environ Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27348605 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of an arrayed CRISPRi library as a resource for essential gene function studies in Streptococcus mutans.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Jan 11;12(1):e0314923. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03149-23. Epub 2023 Dec 6. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 38054713 Free PMC article.
-
Post-translational modification of Streptococcus sanguinis SpxB influences protein solubility and H2 O2 production.Mol Oral Microbiol. 2021 Oct;36(5):267-277. doi: 10.1111/omi.12348. Epub 2021 Aug 3. Mol Oral Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34314577 Free PMC article.
-
Streptococcus mutans yidC1 and yidC2 Impact Cell Envelope Biogenesis, the Biofilm Matrix, and Biofilm Biophysical Properties.J Bacteriol. 2018 Dec 7;201(1):e00396-18. doi: 10.1128/JB.00396-18. Print 2019 Jan 1. J Bacteriol. 2018. PMID: 30322852 Free PMC article.
-
Expanding the genetic toolbox for the obligate human pathogen Streptococcus pyogenes.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024 Jun 7;12:1395659. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1395659. eCollection 2024. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38911550 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barsamian-Wunsch P, Park JH, Watson MR, Tinanoff N, Minah GE. 2004. Microbiological screening for cariogenic bacteria in children 9 to 36 months of age. Pediatr. Dent. 26:231–239 - PubMed
-
- Bowden GH. 1990. Microbiology of root surface caries in humans. J. Dent. Res. 69:1205–1210 - PubMed
-
- Nobre dos Santos M, Melo dos Santos L, Francisco SB, Cury JA. 2002. Relationship among dental plaque composition, daily sugar exposure and caries in the primary dentition. Caries Res. 36:347–352 - PubMed
-
- Thenisch NL, Bachmann LM, Imfeld T, Leisebach Minder T, Steurer J. 2006. Are mutans streptococci detected in preschool children a reliable predictive factor for dental caries risk? A systematic review. Caries Res. 40:366–374 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

