Novel proteomic approach (PUNCH-P) reveals cell cycle-specific fluctuations in mRNA translation
- PMID: 23934657
- PMCID: PMC3759699
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.219105.113
Novel proteomic approach (PUNCH-P) reveals cell cycle-specific fluctuations in mRNA translation
Abstract
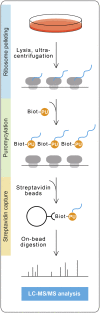
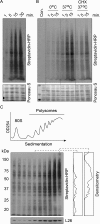
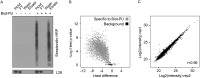
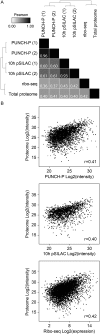
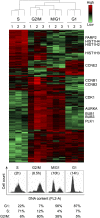
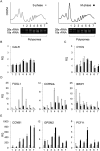
Monitoring protein synthesis is essential to our understanding of gene expression regulation, as protein abundance is thought to be predominantly controlled at the level of translation. Mass-spectrometric and RNA sequencing methods have been recently developed for investigating mRNA translation at a global level, but these still involve technical limitations and are not widely applicable. In this study, we describe a novel system-wide proteomic approach for direct monitoring of translation, termed puromycin-associated nascent chain proteomics (PUNCH-P), which is based on incorporation of biotinylated puromycin into newly synthesized proteins under cell-free conditions followed by streptavidin affinity purification and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry analysis. Using PUNCH-P, we measured cell cycle-specific fluctuations in synthesis for >5000 proteins in mammalian cells, identified proteins not previously implicated in cell cycle processes, and generated the first translational profile of a whole mouse brain. This simple and economical technique is broadly applicable to any cell type and tissue, enabling the identification and quantification of rapid proteome responses under various biological conditions.
Keywords: PUNCH-P; cell cycle; protein synthesis; proteomics; puromycin; translation.
Figures
References
-
- Calkhoven CF, Muller C, Leutz A 2002. Translational control of gene expression and disease. Trends Mol Med 8: 577–583 - PubMed
-
- Clark IE, Wyckoff D, Gavis ER 2000. Synthesis of the posterior determinant Nanos is spatially restricted by a novel cotranslational regulatory mechanism. Curr Biol 10: 1311–1314 - PubMed
-
- Cox J, Mann M 2008. MaxQuant enables high peptide identification rates, individualized p.p.b.-range mass accuracies and proteome-wide protein quantification. Nat Biotechnol 26: 1367–1372 - PubMed
-
- Cox J, Neuhauser N, Michalski A, Scheltema RA, Olsen JV, Mann M 2011. Andromeda: A peptide search engine integrated into the MaxQuant environment. J Proteome Res 10: 1794–1805 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
