Characterising cytokine gene expression signatures in patients with severe sepsis
- PMID: 23935244
- PMCID: PMC3713593
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/164246
Characterising cytokine gene expression signatures in patients with severe sepsis
Abstract
Introduction: Severe sepsis in humans may be related to an underlying profound immune suppressive state. We investigated the link between gene expression of immune regulatory cytokines and the range of illness severity in patients with infection and severe sepsis.
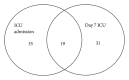
Methods: A prospective observational study included 54 ICU patients with severe sepsis, 53 patients with infection without organ failure, and 20 healthy controls. Gene expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) was measured using real-time polymerase chain reaction.
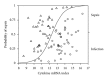
Results: Infection differed from health by decreased expression of the IL2, and IL23 and greater expression of IL10 and IL27. Severe sepsis differed from infection by having decreased IL7, IL23, IFN γ , and TNF α gene expression. An algorithm utilising mRNA copy number for TNF α , IFN γ , IL7, IL10, and IL23 accurately distinguished sepsis from severe sepsis with a receiver operator characteristic value of 0.88. Gene expression was similar with gram-positive and gram-negative infection and was similar following medical and surgical severe sepsis. Severity of organ failure was associated with serum IL6 protein levels but not with any index of cytokine gene expression in PBMCs.
Conclusions: Immune regulatory cytokine gene expression in PBMC provides a robust method of modelling patients' response to infection.
Figures
References
-
- Vincent JL, Sakr Y, Sprung CL, et al. Sepsis in European intensive care units: results of the SOAP study. Critical Care Medicine. 2006;34(2):344–353. - PubMed
-
- O’Dwyer MJ, Mankan AK, Stordeur P, et al. The occurrence of severe sepsis and septic shock are related to distinct patterns of cytokine gene expression. Shock. 2006;26(6):544–550. - PubMed
-
- O’Dwyer MJ, Mankan AK, White M, et al. The human response to infection is associated with distinct patterns of interleukin 23 and interleukin 27 expression. Intensive Care Medicine. 2008;34(4):683–691. - PubMed
-
- White M, Martin-Loeches I, Lawless MW, et al. Hospital-acquired pneumonia after lung resection surgery is associated with characteristic cytokine gene expression. Chest. 2011;139(3):626–632. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical