Gene × physical activity interactions in obesity: combined analysis of 111,421 individuals of European ancestry
- PMID: 23935507
- PMCID: PMC3723486
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003607
Gene × physical activity interactions in obesity: combined analysis of 111,421 individuals of European ancestry
Abstract
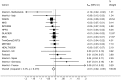
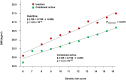
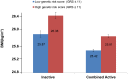
Numerous obesity loci have been identified using genome-wide association studies. A UK study indicated that physical activity may attenuate the cumulative effect of 12 of these loci, but replication studies are lacking. Therefore, we tested whether the aggregate effect of these loci is diminished in adults of European ancestry reporting high levels of physical activity. Twelve obesity-susceptibility loci were genotyped or imputed in 111,421 participants. A genetic risk score (GRS) was calculated by summing the BMI-associated alleles of each genetic variant. Physical activity was assessed using self-administered questionnaires. Multiplicative interactions between the GRS and physical activity on BMI were tested in linear and logistic regression models in each cohort, with adjustment for age, age(2), sex, study center (for multicenter studies), and the marginal terms for physical activity and the GRS. These results were combined using meta-analysis weighted by cohort sample size. The meta-analysis yielded a statistically significant GRS × physical activity interaction effect estimate (Pinteraction = 0.015). However, a statistically significant interaction effect was only apparent in North American cohorts (n = 39,810, Pinteraction = 0.014 vs. n = 71,611, Pinteraction = 0.275 for Europeans). In secondary analyses, both the FTO rs1121980 (Pinteraction = 0.003) and the SEC16B rs10913469 (Pinteraction = 0.025) variants showed evidence of SNP × physical activity interactions. This meta-analysis of 111,421 individuals provides further support for an interaction between physical activity and a GRS in obesity disposition, although these findings hinge on the inclusion of cohorts from North America, indicating that these results are either population-specific or non-causal.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Curtin LR, McDowell MA, Tabak CJ, et al. (2006) Prevalence of overweight and obesity in the United States, 1999–2004. JAMA 295: 1549–1555. - PubMed
-
- Thorleifsson G, Walters GB, Gudbjartsson DF, Steinthorsdottir V, Sulem P, et al. (2009) Genome-wide association yields new sequence variants at seven loci that associate with measures of obesity. Nat Genet 41: 18–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 5P30DK46200/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA087969/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL043851/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA055075/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA155626/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY015473/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- HL080467/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK080140/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK46200/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U54CA155626/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK093757/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HL073168/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL34594/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK093757/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK058845/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004728/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DK062370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HL043851/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA134958/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- EY015473/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK070756/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK072193/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- CA87969/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- DK58845/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HL088521/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK091718/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- MC_U106179473/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- CA49449/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01HG004399/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UU_12015/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 DK062370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- CA047988/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK046200/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK072193/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- MC_U106179471/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- DK091718/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K24 DK080140/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL034594/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- CA134958/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01HG004728-02/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL071981/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA047988/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- DK062370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL080467/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020572/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 HL088521/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA049449/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA055075/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL073168/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA049449/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HL071981/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004399/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- DK70756/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

