T cells induce pre-metastatic osteolytic disease and help bone metastases establishment in a mouse model of metastatic breast cancer
- PMID: 23935856
- PMCID: PMC3730734
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0068171
T cells induce pre-metastatic osteolytic disease and help bone metastases establishment in a mouse model of metastatic breast cancer
Abstract
Bone metastases, present in 70% of patients with metastatic breast cancer, lead to skeletal disease, fractures and intense pain, which are all believed to be mediated by tumor cells. Engraftment of tumor cells is supposed to be preceded by changes in the target tissue to create a permissive microenvironment, the pre-metastatic niche, for the establishment of the metastatic foci. In bone metastatic niche, metastatic cells stimulate bone consumption resulting in the release of growth factors that feed the tumor, establishing a vicious cycle between the bone remodeling system and the tumor itself. Yet, how the pre-metastatic niches arise in the bone tissue remains unclear. Here we show that tumor-specific T cells induce osteolytic bone disease before bone colonization. T cells pro-metastatic activity correlate with a pro-osteoclastogenic cytokine profile, including RANKL, a master regulator of osteoclastogenesis. In vivo inhibition of RANKL from tumor-specific T cells completely blocks bone loss and metastasis. Our results unveil an unexpected role for RANKL-derived from T cells in setting the pre-metastatic niche and promoting tumor spread. We believe this information can bring new possibilities for the development of prognostic and therapeutic tools based on modulation of T cell activity for prevention and treatment of bone metastasis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
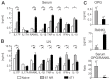

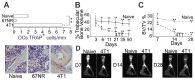

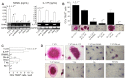
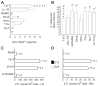

References
-
- Schreiber RD, Old LJ, Smyth MJ (2011) Cancer immunoediting: integrating immunity’s roles in cancer suppression and promotion. Science 331: 1565-1570. doi:10.1126/science.1203486. PubMed: 21436444. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Old LJ, Boyse EA (1964) Immunology of experimental tumors. Annu Rev Med 15: 167-186. doi:10.1146/annurev.me.15.020164.001123. PubMed: 14139934. - DOI - PubMed
-
- DuPage M, Mazumdar C, Schmidt LM, Cheung AF, Jacks T (2012) Expression of tumour-specific antigens underlies cancer immunoediting. Nature 482: 405-409. doi:10.1038/nature10803. PubMed: 22318517. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2011) Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 144: 646-674. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.013. PubMed: 21376230. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

