Evolution of primary HIV drug resistance in a subtype C dominated epidemic in Mozambique
- PMID: 23935858
- PMCID: PMC3728366
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0068213
Evolution of primary HIV drug resistance in a subtype C dominated epidemic in Mozambique
Abstract
Objective: In Mozambique, highly active antiretroviral treatment (HAART) was introduced in 2004 followed by decentralization and expansion, resulting in a more than 20-fold increase in coverage by 2009. Implementation of HIV drug resistance threshold surveys (HIVDR-TS) is crucial in order to monitor the emergence of transmitted viral resistance, and to produce evidence-based recommendations to support antiretroviral (ARV) policy in Mozambique.
Methods: World Health Organization (WHO) methodology was used to evaluate transmitted drug resistance (TDR) in newly diagnosed HIV-1 infected pregnant women attending ante-natal clinics in Maputo and Beira to non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTI), nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTI) and protease inhibitors (PI). Subtypes were assigned using REGA HIV-1 subtyping tool and phylogenetic trees constructed using MEGA version 5.
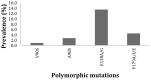
Results: Although mutations associated with resistance to all three drug were detected in these surveys, transmitted resistance was analyzed and classified as <5% in Maputo in both surveys for all three drug classes. Transmitted resistance to NNRTI in Beira in 2009 was classified between 5-15%, an increase from 2007 when no NNRTI mutations were found. All sequences clustered with subtype C.
Conclusions: Our results show that the epidemic is dominated by subtype C, where the first-line option based on two NRTI and one NNRTI is still effective for treatment of HIV infection, but intermediate levels of TDR found in Beira reinforce the need for constant evaluation with continuing treatment expansion in Mozambique.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- UNAIDS (2012) UNAIDS Report on the global AIDS epidemic. [online]. Disponível na URL: http: //www.unaids.org/globalreport/default.htm [Acessado em 03 de Maio de 2013].
-
- MISAU (2007) Boletim epidemioloógico do ministério da Saúde de Moçambique MISAU- Resultados da ronda serologica de 2007.
-
- MISAU (2009) Boletim epidemiológico do ministério da Saúde de Moçambique MISAU- Resultados da ronda serologica.
-
- INS/INE (2010) Inquérito Nacional de prevalência, riscos comportamentais e informação sobre o HIV e SIDA em Moçambique, Relatório 2010.
-
- MOH, Ministry of health HIV/AIDS website (2010) Available: http: //www.misau.gov.mz/pt/hiv_sida/dados_tarv_nacionais.Acessed: 2012 April 22.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

