Application of structural equation models for elucidating the ecological drivers of Anopheles sinensis in the three gorges reservoir
- PMID: 23935887
- PMCID: PMC3728343
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0068766
Application of structural equation models for elucidating the ecological drivers of Anopheles sinensis in the three gorges reservoir
Abstract
Objective: To identify the major ecological drivers for malaria vector density using the structural equation model (SEM) in the Three Gorges Reservoir.
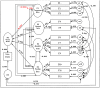
Method: An 11-year longitudinal surveillance of malaria vector as well as its related ecological factors was carried out in the Three Gorges Reservoir. The Delphi method was used to identify associated ecological factors. The structural equation model was repeatedly corrected and improved by the corrected index, combined with the actual situation. The final model was defined by relative simplicity, best fitting as well as the practicality.
Result: The final model indicated that the direct effects of temperature, livestock, humidity, and breeding on the vector were 0.015, -0.228, 0.450, 0.516 respectively, their total effects on the vector were 0.359, -0.112, 0.850, and 0.043 through different pathways.
Conclusion: SEM was effective and convenient in elucidating the mechanism by which malaria vector dynamics operated in this study. It identified that the breeding had the highest direct effect on vector and played a key role for mediating effect of temperature and humidity.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Spatial-temporal variation and primary ecological drivers of Anopheles sinensis human biting rates in malaria epidemic-prone regions of China.PLoS One. 2015 Jan 22;10(1):e0116932. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0116932. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25611483 Free PMC article.
-
Application of Auto-regressive Linear Model in Understanding the Effect of Climate on Malaria Vectors Dynamics in the Three Gorges Reservoir.Biomed Environ Sci. 2014 Oct;27(10):811-4. doi: 10.3967/bes2014.117. Biomed Environ Sci. 2014. PMID: 25341817
-
Modeling of the ecological niches of the anopheles spp in Ecuador by the use of geo-informatic tools.Spat Spatiotemporal Epidemiol. 2017 Jun;21:1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.sste.2016.12.001. Epub 2016 Dec 31. Spat Spatiotemporal Epidemiol. 2017. PMID: 28552183
-
[Strategies and studies of malaria vector control in Jiangsu Province].Zhongguo Xue Xi Chong Bing Fang Zhi Za Zhi. 2020 Oct 26;32(5):459-463. doi: 10.16250/j.32.1374.2020174. Zhongguo Xue Xi Chong Bing Fang Zhi Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 33185055 Review. Chinese.
-
Review of the Minimus Complex of Anopheles, main malaria vector in Southeast Asia: from taxonomic issues to vector control strategies.Trop Med Int Health. 2006 Jan;11(1):102-14. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3156.2005.01536.x. Trop Med Int Health. 2006. PMID: 16398761 Review.
Cited by
-
Disarmament is the New War, Gold is the New Opium, and Ecohealth is the Historic Victim.Environ Health Insights. 2019 Jul 15;13:1178630219862241. doi: 10.1177/1178630219862241. eCollection 2019. Environ Health Insights. 2019. PMID: 31320800 Free PMC article.
-
Nowcasting Vector Mosquito Abundance and Determining Its Association With Malaria Epidemics in South Korea.Transbound Emerg Dis. 2025 Jan 17;2025:9959287. doi: 10.1155/tbed/9959287. eCollection 2025. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2025. PMID: 40302739 Free PMC article.
-
Spatio-temporal analysis of malaria vectors in national malaria surveillance sites in China.Parasit Vectors. 2015 Mar 7;8:146. doi: 10.1186/s13071-015-0741-5. Parasit Vectors. 2015. PMID: 25888910 Free PMC article.
-
A mixed method to evaluate burden of malaria due to flooding and waterlogging in Mengcheng County, China: a case study.PLoS One. 2014 May 15;9(5):e97520. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0097520. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24830808 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial-temporal variation and primary ecological drivers of Anopheles sinensis human biting rates in malaria epidemic-prone regions of China.PLoS One. 2015 Jan 22;10(1):e0116932. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0116932. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25611483 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Three Gorges Project. Available: http://www.ctgpc.com/introduction/introduction_a.php. Accessed 2011 Nov 26.
-
- Jiang S, Xiao B, Wu C (2007) The results of analysis and surveillance on the relevant factors affecting malaria prevalence before the Three Gorge Dam construction. J Trop Dis Parasitol 5: 73–78.
-
- Plowright RK, Sokolow SH, Gorman ME (2008) Causal inference in disease ecology: investigating ecological drivers of disease emergence. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment 6: 420–429.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical