Dopaminergic neuronal imaging in genetic Parkinson's disease: insights into pathogenesis
- PMID: 23935950
- PMCID: PMC3720622
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0069190
Dopaminergic neuronal imaging in genetic Parkinson's disease: insights into pathogenesis
Abstract
Objectives: To compare the dopaminergic neuronal imaging features of different subtypes of genetic Parkinson's Disease.
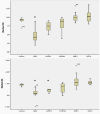
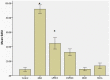
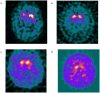
Methods: A retrospective study of genetic Parkinson's diseases cases in which DaTSCAN (123I-FP-CIT) had been performed. Specific non-displaceable binding was calculated for bilateral caudate and putamen for each case. The right:left asymmetry index and striatal asymmetry index was calculated.
Results: Scans were available from 37 cases of monogenetic Parkinson's disease (7 glucocerebrosidase (GBA) mutations, 8 alpha-synuclein, 3 LRRK2, 7 PINK1, 12 Parkin). The asymmetry of radioligand uptake for Parkinson's disease with GBA or LRRK2 mutations was greater than that for Parkinson's disease with alpha synuclein, PINK1 or Parkin mutations.
Conclusions: The asymmetry of radioligand uptake in Parkinsons disease associated with GBA or LRRK2 mutations suggests that interactions with additional genetic or environmental factors may be associated with dopaminergic neuronal loss.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Lees AJ, Hardy J, Resvez T (2009) Parkinson's disease. Lancet 373: 2055–2066. - PubMed
-
- Schapira AH, Jenner P (2011) Etiology and pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord 26: 1049–1055. - PubMed
-
- Lesage S, Anheim M, Condroyer C, Pollak P, Durif F, et al. (2011) Large scale screening of the Gaucher's disease related glucocerebrosidas gene in Europeans with Parkinson's disease. Hum Mol Genet 20: 202–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

