Integrated analysis of drug-induced gene expression profiles predicts novel hERG inhibitors
- PMID: 23936032
- PMCID: PMC3720659
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0069513
Integrated analysis of drug-induced gene expression profiles predicts novel hERG inhibitors
Abstract
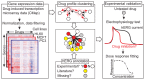
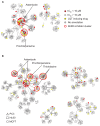
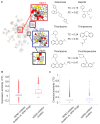
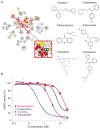
Growing evidence suggests that drugs interact with diverse molecular targets mediating both therapeutic and toxic effects. Prediction of these complex interactions from chemical structures alone remains challenging, as compounds with different structures may possess similar toxicity profiles. In contrast, predictions based on systems-level measurements of drug effect may reveal pharmacologic similarities not evident from structure or known therapeutic indications. Here we utilized drug-induced transcriptional responses in the Connectivity Map (CMap) to discover such similarities among diverse antagonists of the human ether-à-go-go related (hERG) potassium channel, a common target of promiscuous inhibition by small molecules. Analysis of transcriptional profiles generated in three independent cell lines revealed clusters enriched for hERG inhibitors annotated using a database of experimental measurements (hERGcentral) and clinical indications. As a validation, we experimentally identified novel hERG inhibitors among the unannotated drugs in these enriched clusters, suggesting transcriptional responses may serve as predictive surrogates of cardiotoxicity complementing existing functional assays.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Keiser MJ, Setola V, Irwin JJ, Laggner C, Abbas AI et al. (2009) Predicting new molecular targets for known drugs. Nature 462: 175-181. doi:10.1038/nature08506. PubMed: 19881490. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Campillos M, Kuhn M, Gavin AC, Jensen LJ, Bork P (2008) Drug target identification using side-effect similarity. Science 321: 263-266. doi:10.1126/science.1158140. PubMed: 18621671. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fliri AF, Loging WT, Thadeio PF, Volkmann RA (2005) Analysis of drug-induced effect patterns to link structure and side effects of medicines. Nat Chem Biol 1: 389-397. doi:10.1038/nchembio747. PubMed: 16370374. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Xie L, Kinnings SL, Bourne PE (2012) Novel computational approaches to polypharmacology as a means to define responses to individual drugs. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 52: 361-379. doi:10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-010611-134630. PubMed: 22017683. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

