Challenges in using cultured primary rodent hepatocytes or cell lines to study hepatic HDL receptor SR-BI regulation by its cytoplasmic adaptor PDZK1
- PMID: 23936087
- PMCID: PMC3720616
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0069725
Challenges in using cultured primary rodent hepatocytes or cell lines to study hepatic HDL receptor SR-BI regulation by its cytoplasmic adaptor PDZK1
Abstract
Background: PDZK1 is a four PDZ-domain containing cytoplasmic protein that binds to a variety of membrane proteins via their C-termini and can influence the abundance, localization and/or function of its target proteins. One of these targets in hepatocytes in vivo is the HDL receptor SR-BI. Normal hepatic expression of SR-BI protein requires PDZK1 - <5% of normal hepatic SR-BI is seen in the livers of PDZK1 knockout mice. Progress has been made in identifying features of PDZK1 required to control hepatic SR-BI in vivo using hepatic expression of wild-type and mutant forms of PDZK1 in wild-type and PDZK1 KO transgenic mice. Such in vivo studies are time consuming and expensive, and cannot readily be used to explore many features of the underlying molecular and cellular mechanisms.
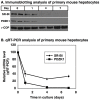
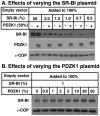
Methodology/principal findings: Here we have explored the potential to use either primary rodent hepatocytes in culture using 2D collagen gels with newly developed optimized conditions or PDZK1/SR-BI co-transfected cultured cell lines (COS, HEK293) for such studies. SR-BI and PDZK1 protein and mRNA expression levels fell rapidly in primary hepatocyte cultures, indicating this system does not adequately mimic hepatocytes in vivo for analysis of the PDZK1 dependence of SR-BI. Although PDZK1 did alter SR-BI protein expression in the cell lines, its influence was independent of SR-BI's C-terminus, and thus is not likely to occur via the same mechanism as that which occurs in hepatocytes in vivo.
Conclusions/significance: Caution must be exercised in using primary hepatocytes or cultured cell lines when studying the mechanism underlying the regulation of hepatic SR-BI by PDZK1. It may be possible to use SR-BI and PDZK1 expression as sensitive markers for the in vivo-like state of hepatocytes to further improve primary hepatocyte cell culture conditions.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Noncanonical role of the PDZ4 domain of the adaptor protein PDZK1 in the regulation of the hepatic high density lipoprotein receptor scavenger receptor class B, type I (SR-BI).J Biol Chem. 2013 Jul 5;288(27):19845-60. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.460170. Epub 2013 May 17. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23720744 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of the PDZ1 domain of PDZK1 blocks the activity of hepatic scavenger receptor, class B, type I by altering its abundance and cellular localization.J Biol Chem. 2008 Aug 8;283(32):22097-104. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M800029200. Epub 2008 Jun 10. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18544532 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of the PDZ3 domain of the adaptor protein PDZK1 as a second, physiologically functional binding site for the C terminus of the high density lipoprotein receptor scavenger receptor class B type I.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jul 15;286(28):25171-86. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.242362. Epub 2011 May 23. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21602281 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the adaptor protein PDZK1 in controlling the HDL receptor SR-BI.Curr Opin Lipidol. 2009 Jun;20(3):236-41. doi: 10.1097/MOL.0b013e32832aee82. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2009. PMID: 19421056 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of SR-BI-mediated high-density lipoprotein metabolism by the tissue-specific adaptor protein PDZK1.Curr Opin Lipidol. 2005 Apr;16(2):147-52. doi: 10.1097/01.mol.0000162319.54795.e5. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2005. PMID: 15767854 Review.
Cited by
-
Lipid abnormalities in alpha/beta2-syntrophin null mice are independent from ABCA1.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 May;1851(5):527-36. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2015.01.012. Epub 2015 Jan 24. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25625330 Free PMC article.
-
Scavenger Receptor BI Deficiency in Mice Is Associated With Plasma Ceramide and Sphingomyelin Accumulation and a Reduced Cholesteryl Ester Fatty Acid Length and Unsaturation Degree.J Lipid Atheroscler. 2024 Jan;13(1):69-79. doi: 10.12997/jla.2024.13.1.69. Epub 2023 Nov 6. J Lipid Atheroscler. 2024. PMID: 38299166 Free PMC article.
-
Differential basolateral-apical distribution of scavenger receptor, class B, type I in cultured cells and the liver.Histochem Cell Biol. 2014 Dec;142(6):645-55. doi: 10.1007/s00418-014-1251-9. Epub 2014 Jul 25. Histochem Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 25059650 Free PMC article.
-
FoxO transcription factors are required for hepatic HDL cholesterol clearance.J Clin Invest. 2018 Apr 2;128(4):1615-1626. doi: 10.1172/JCI94230. Epub 2018 Mar 19. J Clin Invest. 2018. PMID: 29408809 Free PMC article.
-
Procollagen C-endopeptidase Enhancer Protein 2 (PCPE2) Reduces Atherosclerosis in Mice by Enhancing Scavenger Receptor Class B1 (SR-BI)-mediated High-density Lipoprotein (HDL)-Cholesteryl Ester Uptake.J Biol Chem. 2015 Jun 19;290(25):15496-15511. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.646240. Epub 2015 May 6. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25947382 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gordon DJ, Rifkind BM (1989) High-density lipoprotein–the clinical implications of recent studies. N Engl J Med 321: 1311–1316. - PubMed
-
- Kannel BW, Castelli WP, Gordon T, McNamara PM (1971) Serum cholesterol, lipoproteins, and the risk of coronary heart disease. The Framingham study. Ann Intern Med 74: 1–12. - PubMed
-
- Rigotti A, Miettinen HE, Krieger M (2003) The role of the high-density lipoprotein receptor SR-BI in the lipid metabolism of endocrine and other tissues. Endocr Rev 24: 357–387. - PubMed
-
- Kozarsky KF, Donahee MH, Rigotti A, Iqbal SN, Edelman ER, et al. (1997) Overexpression of the HDL receptor SR-BI alters plasma HDL and bile cholesterol levels. Nature 387: 414–417. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

