Involvement of the clock gene Rev-erb alpha in the regulation of glucagon secretion in pancreatic alpha-cells
- PMID: 23936124
- PMCID: PMC3723646
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0069939
Involvement of the clock gene Rev-erb alpha in the regulation of glucagon secretion in pancreatic alpha-cells
Abstract
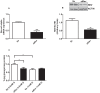
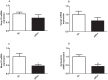
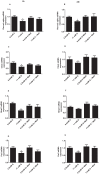
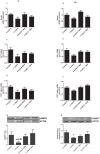
Disruption of pancreatic clock genes impairs pancreatic beta-cell function, leading to the onset of diabetes. Despite the importance of pancreatic alpha-cells in the regulation of glucose homeostasis and in diabetes pathophysiology, nothing is known about the role of clock genes in these cells. Here, we identify the clock gene Rev-erb alpha as a new intracellular regulator of glucagon secretion. Rev-erb alpha down-regulation by siRNA (60-70% inhibition) in alphaTC1-9 cells inhibited low-glucose induced glucagon secretion (p<0.05) and led to a decrease in key genes of the exocytotic machinery. The Rev-erb alpha agonist GSK4112 increased glucagon secretion (1.6 fold) and intracellular calcium signals in alphaTC1-9 cells and mouse primary alpha-cells, whereas the Rev-erb alpha antagonist SR8278 produced the opposite effect. At 0.5 mM glucose, alphaTC1-9 cells exhibited intrinsic circadian Rev-erb alpha expression oscillations that were inhibited by 11 mM glucose. In mouse primary alpha-cells, glucose induced similar effects (p<0.001). High glucose inhibited key genes controlled by AMPK such as Nampt, Sirt1 and PGC-1 alpha in alphaTC1-9 cells (p<0.05). AMPK activation by metformin completely reversed the inhibitory effect of glucose on Nampt-Sirt1-PGC-1 alpha and Rev-erb alpha. Nampt inhibition decreased Sirt1, PGC-1 alpha and Rev-erb alpha mRNA expression (p<0.01) and glucagon release (p<0.05). These findings identify Rev-erb alpha as a new intracellular regulator of glucagon secretion via AMPK/Nampt/Sirt1 pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Muhlbauer E, Wolgast S, Finckh U, Peschke D, Peschke E (2004) Indication of circadian oscillations in the rat pancreas. FEBS Lett 564: 91–96. - PubMed
-
- Panda S, Antoch MP, Miller BH, Su AI, Schook AB, et al. (2002) Coordinated transcription of key pathways in the mouse by the circadian clock. Cell 109: 307–320. - PubMed
-
- Vieira E, Nilsson EC, Nerstedt A, Ormestad M, Long YC, et al. (2008) Relationship between AMPK and the transcriptional balance of clock-related genes in skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 295: E1032–1037. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

