Improvement of pharmacokinetics behavior of apocynin by nitrone derivatization: comparative pharmacokinetics of nitrone-apocynin and its parent apocynin in rats
- PMID: 23936162
- PMCID: PMC3728092
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0070189
Improvement of pharmacokinetics behavior of apocynin by nitrone derivatization: comparative pharmacokinetics of nitrone-apocynin and its parent apocynin in rats
Abstract
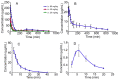
Apocynin, a potent inhibitor of NADPH-oxidase, was widely studied for activities in diseases such as inflammation-mediated disorders, asthma and cardiovascular diseases. In our recent study, a novel nitrone derivative of apocynin, AN-1, demonstrated potent inhibition to oxidative injury and to high expression of gp91(phox) subunit of NADPH-oxidase induced by tert-butyl hydroperoxide (t-BHP) in RAW 264.7 macrophage cells, and displayed promising preclinical protective effect against lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced acute lung injury in rats. In this work, the pharmacokinetic behaviors of AN-1 in Sprague-Dawley rats with single intravenous and intragastric doses were investigated for further development. Furthermore, apocynin's pharmacokinetics remain lacking, even though its pharmacological action has been extensively evaluated. The pharmacokinetics of parent apocynin were also comparatively characterized. A simple HPLC method was developed and validated to determine both AN-1 and apocynin in rat plasma. The chromatographic separation was achieved on an Agilent HC-C18 column (250 mm×4.6 mm, 5 µm) at an isocratic flow rate of 1.0 mL/min, with the mobile phase of methanol and water (53∶47, v/v) and the UV detection set at 279 nm. Good linearity was established over the concentration range of 0.1-500 µg/mL for AN-1 and 0.2-100 µg/mL for apocynin. The absolute recovery, precision and accuracy were satisfactory. Compared with the parent compound apocynin, AN-1 yielded a much longer T1/2 (AN-1 179.8 min, apocynin 6.1 min) and higher AUC0-t (AN-1 61.89 mmol/L·min, apocynin 2.49 mmol/L·min) after equimolar intravenous dosing (0.302 mmol/kg). The absolute bioavailability of oral AN-1 was 78%, but that of apocynin was only 2.8%. The significant improvement of pharmacokinetic behavior might be accounted for the effective pharmacodynamic results we documented for the novel nitrone derivative AN-1.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Li JM, Gall NP, Grieve DJ, Chen M, Shah AM (2002) Activation of NADPH oxidase during progression of cardiac hypertrophy to failure. Hypertension 40: 477–484. - PubMed
-
- Impellizzeri D, Mazzon E, Esposito E, Paterniti I, Bramanti P, et al. (2011) Effect of Apocynin, an inhibitor of NADPH oxidase, in the inflammatory process induced by an experimental model of spinal cord injury. Free Radic Res 45: 221–236. - PubMed
-
- Lafeber FP, Beukelman CJ, van den Worm E, van Roy JL, Vianen ME, et al. (1999) Apocynin, a plant-derived, cartilage-saving drug, might be useful in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 38: 1088–1093. - PubMed
-
- Hougee S, Hartog A, Sanders A, Graus YM, Hoijer MA, et al. (2006) Oral administration of the NADPH-oxidase inhibitor apocynin partially restores diminished cartilage proteoglycan synthesis and reduces inflammation in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 531: 264–269. - PubMed
-
- Stolk J, Hiltermann TJ, Dijkman JH, Verhoeven AJ (1994) Characteristics of the inhibition of NADPH oxidase activation in neutrophils by apocynin, a methoxy-substituted catechol. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 11: 95–102. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

