Tocilizumab induced acquired factor XIII deficiency in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 23936360
- PMCID: PMC3731329
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0069944
Tocilizumab induced acquired factor XIII deficiency in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
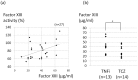
Factor XIII is one of the twelve coagulation factors and also known as a fibrin-stabilizing factor. In 2012, we encountered a male RA patient with hemorrhagic factor XIII deficiency who had been treated with tocilizumab for two years. There are few reports regarding the relationship between tocilizumab (a humanized monoclonal antibody against the interleukin-6 receptor (IL-6R)) and factor XIII. We measured the factor XIII activity levels in the plasma of 40 RA patients (10 patients treated without biologics, 30 patients treated with biologics (15 patients treated with necrosis factor inhibitors and 15 patients treated with tocilizumab)) and 19 healthy controls. Consequently, the tocilizumab group exhibited lower levels than the other three groups according to the Steel-Dwass test (P<0.01). Furthermore, we compared the plasma factor XIII activity levels and the plasma factor XIII concentrations in the RA patients treated with biologics. Pearson's correlation test was used to assess the relationship between the factor XIII activity levels and the plasma factor XIII concentrations (r=0.449, P=0.019). According to the multiple regression analysis, the treatment with tocilizumab is an independent risk factor for plasma factor XIII reduction in RA patients. In conclusion, RA patients treated with tocilizumab, an IL-6R blocker, are at risk of developing acquired factor XIII deficiency. The mechanisms underlying the reduced factor XIII activity observed in RA patients treated with tocilizumab may result from the quantitative reduction in the plasma. These data imply that IL-6 plays an important role in maintaining the factor XIII activity level.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Komáromi I, Bagoly Z, Muszbek L (2011) Factor XIII: novel structural and functional aspects. J Thromb Haemost 9: 9–20. - PubMed
-
- Muszbek L, Bagoly Z, Bereczky Z, Katona E (2008) The involvement of blood coagulation factor XIII in fibrinolysis and thrombosis. Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem 6: 190–205. - PubMed
-
- Muszbek L, Yee VC, Hevessy Z (1999) Blood coagulation factor XIII: structure and function. Thromb Res 94: 271–305. - PubMed
-
- Ichinose A, McMullen BA, Fujikawa K, Davie EW (1986) Amino acid sequence of the b subunit of human factor XIII, a protein composed of ten repetitive segments. Biochemistry 25: 4633–4638. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

