Heat stress reduces intestinal barrier integrity and favors intestinal glucose transport in growing pigs
- PMID: 23936392
- PMCID: PMC3731365
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0070215
Heat stress reduces intestinal barrier integrity and favors intestinal glucose transport in growing pigs
Abstract
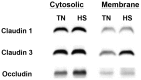
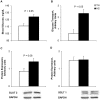
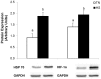
Excessive heat exposure reduces intestinal integrity and post-absorptive energetics that can inhibit wellbeing and be fatal. Therefore, our objectives were to examine how acute heat stress (HS) alters intestinal integrity and metabolism in growing pigs. Animals were exposed to either thermal neutral (TN, 21°C; 35-50% humidity; n=8) or HS conditions (35°C; 24-43% humidity; n=8) for 24 h. Compared to TN, rectal temperatures in HS pigs increased by 1.6°C and respiration rates by 2-fold (P<0.05). As expected, HS decreased feed intake by 53% (P<0.05) and body weight (P<0.05) compared to TN pigs. Ileum heat shock protein 70 expression increased (P<0.05), while intestinal integrity was compromised in the HS pigs (ileum and colon TER decreased; P<0.05). Furthermore, HS increased serum endotoxin concentrations (P=0.05). Intestinal permeability was accompanied by an increase in protein expression of myosin light chain kinase (P<0.05) and casein kinase II-α (P=0.06). Protein expression of tight junction (TJ) proteins in the ileum revealed claudin 3 and occludin expression to be increased overall due to HS (P<0.05), while there were no differences in claudin 1 expression. Intestinal glucose transport and blood glucose were elevated due to HS (P<0.05). This was supported by increased ileum Na(+)/K(+) ATPase activity in HS pigs. SGLT-1 protein expression was unaltered; however, HS increased ileal GLUT-2 protein expression (P=0.06). Altogether, these data indicate that HS reduce intestinal integrity and increase intestinal stress and glucose transport.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Kosatsky T (2005) The 2003 European heat waves. Euro Surveill 10: 148–149. - PubMed
-
- Patz JA, Campbell-Lendrum D, Holloway T, Foley JA (2005) Impact of regional climate change on human health. Nature 438: 310–317. - PubMed
-
- LoVecchio F, Pizon AF, Berret C, Balls A (2007) Outcomes after environmental hyperthermia. Am J Emergency Med 25: 442–444. - PubMed
-
- St-Pierre NR, Cobanov B, Schnitkey G (2003) Economic Losses from Heat Stress by US Livestock Industries1. Journal of dairy science 86: E52–E77.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

