Pancreaticoduodenectomy combined with vascular resection and reconstruction for patients with locally advanced pancreatic cancer: a multicenter, retrospective analysis
- PMID: 23936411
- PMCID: PMC3732270
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0070340
Pancreaticoduodenectomy combined with vascular resection and reconstruction for patients with locally advanced pancreatic cancer: a multicenter, retrospective analysis
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study was to present the therapeutic outcome of patients with locally advanced pancreatic cancer treated with pancreatoduodenectomy combined with vascular resection and reconstruction in addition to highlighting the mortality/morbidity and main prognostic factors associated with this treatment.
Materials and methods: We retrospectively analyzed the clinical and pathological data of a total of 566 pancreatic cancer patients who were treated with PD from five teaching hospitals during the period of December 2006-December 2011. This study included 119 (21.0%) patients treated with PD combined with vascular resection and reconstruction. We performed a detailed statistical analysis of various factors, including postoperative complications, operative mortality, survival rate, operative time, pathological type, and lymph node metastasis.
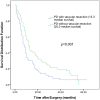
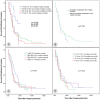
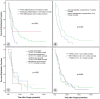
Results: The median survival time of the 119 cases that received PD combined with vascular resection was 13.3 months, and the 1-, 2-, and 3-year survival rates were 30.3%, 14.1%, and 8.1%, respectively. The postoperative complication incidence was 23.5%, and the mortality rate was 6.7%. For the combined vascular resection group, complications occurred in 28 cases (23.5%). For the group without vascular resection, complications occurred in 37 cases (8.2%). There was significant difference between the two groups (p = 0.001). The degree of tumor differentiation and the occurrence of complications after surgery were independent prognostic factors that determined the patients' long-term survival.
Conclusions: Compared with PD without vascular resection, PD combined with vascular resection and reconstruction increased the incidence of postoperative complications. However, PD combined with vascular resection and reconstruction could achieve the complete removal of tumors without significantly increasing the mortality rate, and the median survival time was higher than that of patients who underwent palliative treatment. In addition, the two independent factors affecting the postoperative survival time were the degree of tumor differentiation and the presence or absence of postoperative complications.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Postoperative Outcomes of Tangential versus Segmental Resection and End-to-end Reconstruction of the Superior Mesenterico-Portal Vein During Pancreatoduodenectomy for Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma: A Single-Center Experience.Anticancer Res. 2021 Oct;41(10):5123-5130. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.15329. Anticancer Res. 2021. PMID: 34593463 Clinical Trial.
-
Postoperative morbidity and long-term survival after pancreaticoduodenectomy with superior mesenterico-portal vein resection.J Gastrointest Surg. 2006 Sep-Oct;10(8):1106-15. doi: 10.1016/j.gassur.2006.04.002. J Gastrointest Surg. 2006. PMID: 16966029
-
Pancreaticoduodenectomy with vascular reconstruction for adenocarcinoma of the pancreas with borderline resectability.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Dec 14;20(46):17448-55. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i46.17448. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25516657 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of expanding indications on surgical and oncological outcome in 1434 consecutive pancreatoduodenectomies.HPB (Oxford). 2019 Jul;21(7):865-875. doi: 10.1016/j.hpb.2018.10.020. Epub 2018 Dec 31. HPB (Oxford). 2019. PMID: 30606684
-
Justifying vein resection with pancreatoduodenectomy.Lancet Oncol. 2016 Mar;17(3):e118-e124. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(15)00463-5. Epub 2016 Mar 2. Lancet Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26972858 Review.
Cited by
-
Radical Resection for Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancers in the Era of New Neoadjuvant Therapy-Arterial Resection, Arterial Divestment and Total Pancreatectomy.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Apr 10;13(8):1818. doi: 10.3390/cancers13081818. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33920314 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The value of combined vein resection in pancreaticoduodenectomy for pancreatic head carcinoma: a meta-analysis.BMC Surg. 2019 Jul 8;19(1):84. doi: 10.1186/s12893-019-0540-6. BMC Surg. 2019. PMID: 31286916 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenteric-Portal Vein Resection during Pancreatectomy for Pancreatic Cancer.Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2015;2015:659730. doi: 10.1155/2015/659730. Epub 2015 Nov 1. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2015. PMID: 26609307 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic factors after pancreatoduodenectomy with en bloc portal venous resection for pancreatic cancer.Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2016 Feb;401(1):63-9. doi: 10.1007/s00423-015-1363-2. Epub 2016 Jan 6. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2016. PMID: 26739620
-
Segmental portal/superior mesenteric vein resection and reconstruction with the iliac vein after pancreatoduodenectomy.J Int Med Res. 2016 Dec;44(6):1339-1348. doi: 10.1177/0300060516665708. Epub 2016 Nov 10. J Int Med Res. 2016. PMID: 28322103 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pakin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P (2005) Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 55: 74–108. - PubMed
-
- Jemal A, Bray F (2011) Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, et al (2011) Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 61: 69–90. - PubMed
-
- Al-Haddad M, Martin JK, Nguyen J, Pungpapong S, Raimondo M, et al. (2007) Vascular resection and reconstruction for pancreatic malignancy: a single center survival study. J Gastrointest Surg 11: 1168–1174. - PubMed
-
- Christians K, Evans DB (2009) Pancreaticoduodenectomy and vascular resection: persistent controversy and current recommendations. Ann Surg Oncol 16: 789–791. - PubMed
-
- Varadhachary GR, Tamm EP, Abbruzzese JL, Xiong HQ, Crane CH, et al. (2006) Borderline resectable pancreatic cancer: definitions, management, and role of preoperative therapy. Annals of Surgical Oncology 13: 1035–1046. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

