Changes of von Willebrand Factor during Pregnancy in Women with and without von Willebrand Disease
- PMID: 23936623
- PMCID: PMC3736880
- DOI: 10.4084/MJHID.2013.052
Changes of von Willebrand Factor during Pregnancy in Women with and without von Willebrand Disease
Abstract
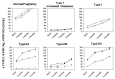
Delivery in von Willebrand disease (VWD) represents a significant hemostatic challenge because of the variable pattern of changes observed during pregnancy of von Willebrand factor (VWF) and factor VIII (FVIII), the protein carried by VWF. Since a wide heterogeneity of phenotypes and of the underlying pathophysiological mechanisms is associated with this disorder, a prompt and careful evaluation of pregnant women with VWD is requested in order to plan the most appropriate treatment at time of parturition. VWF and FVIII increase significantly during pregnancy in normal women, already within the first trimester, reaching levels by far >100 U/dL by the time of parturition. Women with VWD, levels at baseline of VWF and FVIII >30 U/dL have us a high likelihood to achieve normal levels at the end of pregnancy; thus specific anti-hemorrhagic prophylaxis is seldom required. Women with basal level <20 U/dL usually have a poor increase since most of these women carry mutations associated with increased VWF clearance or are compound heterozygous for different VWF mutations; that prevent the achievement of satisfactory hemostatic levels. While women with mutations associated with increased clearance show a full, albeit transitory correction of their hemostatic deficiency after desmopressin administration, compound heterozygous need replacement therapy because they do not respond well to this agent. Patients with abnormal VWF:RCo/VWF:Ag ratio at baseline (e.g. <0.6), typically associated with type 2 VWD, maintain the abnormality throughout pregnancy and VWF:RCo usually does not attain safe levels ≥50 U/dL. These women require replacement therapy with VWF-FVIII concentrates. Delayed post-partum bleeding may occur when replacement therapy is not continued for some days. Tranexamic acid may be useful at discharge to avoid excessive lochia.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pregnancy and delivery in women with von Willebrand disease.Eur J Haematol. 2019 Aug;103(2):73-79. doi: 10.1111/ejh.13250. Epub 2019 May 31. Eur J Haematol. 2019. PMID: 31107984 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bleeding prophylaxis for major surgery in patients with type 2 von Willebrand disease with an intermediate purity factor VIII-von Willebrand factor concentrate (Haemate-P).Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2004 Jun;15(4):323-30. doi: 10.1097/00001721-200406000-00006. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2004. PMID: 15166918 Clinical Trial.
-
Laboratory diagnosis of von Willebrand disease type 1/2E (2A subtype IIE), type 1 Vicenza and mild type 1 caused by mutations in the D3, D4, B1-B3 and C1-C2 domains of the von Willebrand factor gene. Role of von Willebrand factor multimers and the von Willebrand factor propeptide/antigen ratio.Acta Haematol. 2009;121(2-3):128-38. doi: 10.1159/000214853. Epub 2009 Jun 8. Acta Haematol. 2009. PMID: 19506359 Review.
-
Diagnosis of von Willebrand disease type 2N: a simplified method for measurement of factor VIII binding to von Willebrand factor.Am J Hematol. 1998 Aug;58(4):311-8. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1096-8652(199808)58:4<311::aid-ajh11>3.0.co;2-a. Am J Hematol. 1998. PMID: 9692396
-
Management of von Willebrand disease with factor VIII/von Willebrand factor concentrates: results from current studies and surveys.Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2005 Apr;16 Suppl 1:S17-21. doi: 10.1097/01.mbc.0000167658.85143.49. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2005. PMID: 15849522 Review.
Cited by
-
ABO blood group in primary antiphospholipid syndrome: influence in the site of thrombosis?J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2015 Oct;40(3):374-8. doi: 10.1007/s11239-015-1176-8. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2015. PMID: 25638331 Clinical Trial.
-
Fundamentals for a Systematic Approach to Mild and Moderate Inherited Bleeding Disorders: An EHA Consensus Report.Hemasphere. 2019 Sep 17;3(4):e286. doi: 10.1097/HS9.0000000000000286. eCollection 2019 Oct. Hemasphere. 2019. PMID: 31942541 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic regulation of plasma von Willebrand factor levels in health and disease.J Thromb Haemost. 2018 Dec;16(12):2375-2390. doi: 10.1111/jth.14304. Epub 2018 Oct 30. J Thromb Haemost. 2018. PMID: 30246494 Free PMC article. Review.
-
von Willebrand disease and von Willebrand factor.Haemophilia. 2022 May;28 Suppl 4(Suppl 4):11-17. doi: 10.1111/hae.14547. Haemophilia. 2022. PMID: 35521725 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Von Willebrand Disease on Pregnancy, Delivery, and Postpartum Period: A Retrospective Observational Study.Medicina (Kaunas). 2022 Jun 7;58(6):774. doi: 10.3390/medicina58060774. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022. PMID: 35744037 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ACOG. ACOG Practice Bulletin: Clinical Management Guidelines for Obstetrician-Gynecologists. : postpartum haemorrhage. Obstet Gynecol. 2006 2006 Oct;Number 76108:1039–47. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
