Validation of computerized automatic calculation of the sequential organ failure assessment score
- PMID: 23936639
- PMCID: PMC3722890
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/975672
Validation of computerized automatic calculation of the sequential organ failure assessment score
Abstract
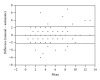
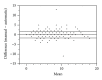
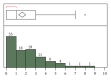
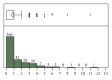
Purpose. To validate the use of a computer program for the automatic calculation of the sequential organ failure assessment (SOFA) score, as compared to the gold standard of manual chart review. Materials and Methods. Adult admissions (age > 18 years) to the medical ICU with a length of stay greater than 24 hours were studied in the setting of an academic tertiary referral center. A retrospective cross-sectional analysis was performed using a derivation cohort to compare automatic calculation of the SOFA score to the gold standard of manual chart review. After critical appraisal of sources of disagreement, another analysis was performed using an independent validation cohort. Then, a prospective observational analysis was performed using an implementation of this computer program in AWARE Dashboard, which is an existing real-time patient EMR system for use in the ICU. Results. Good agreement between the manual and automatic SOFA calculations was observed for both the derivation (N=94) and validation (N=268) cohorts: 0.02 ± 2.33 and 0.29 ± 1.75 points, respectively. These results were validated in AWARE (N=60). Conclusion. This EMR-based automatic tool accurately calculates SOFA scores and can facilitate ICU decisions without the need for manual data collection. This tool can also be employed in a real-time electronic environment.
Figures
References
-
- Knaus WA, Zimmerman JE, Wagner DP, Draper EA, Lawrence DE. APACHE-acute physiology and chronic health evaluation: a physiologically based classification system. Critical Care Medicine. 1981;9(8):591–597. - PubMed
-
- Zimmerman JE, Kramer AA, McNair DS, Malila FM. Acute physiology and chronic health evaluation (APACHE) IV: hospital mortality assessment for today’s critically ill patients. Critical Care Medicine. 2006;34(5):1297–1310. - PubMed
-
- Le Gall J-R, Loirat P, Alperovitch A. A simplified acute physiology score for ICU patients. Critical Care Medicine. 1984;12(11):975–977. - PubMed
-
- Lemeshow S, Teres D, Pastides H. A method for predicting survival and mortality of ICU patients using objectively derived weights. Critical Care Medicine. 1985;13(7):519–525. - PubMed
-
- Vincent J-L, Moreno R, Takala J, et al. The SOFA (Sepsis-related Organ Failure Assessment) score to describe organ dysfunction/failure. Intensive Care Medicine. 1996;22(7):707–710. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

