Trends of postpartum depression in iran: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 23936640
- PMCID: PMC3722792
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/291029
Trends of postpartum depression in iran: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background. Postpartum depression (PPD) is a serious mental health disorder affecting 13% of women in developed communities. The present study reviews available epidemiological publications on PPD-related aspects in Iranian women to help policy makers and health workers to design preventative strategies and further researches. Materials and Methods. A systematic review was constructed based on the computerized literature valid database. The 95% confidence intervals were calculated by random effects models. Metaregression was introduced to explore and explain heterogeneity between studies. Data manipulation and statistical analyses were performed using Stata 11. Results. Overall, 41 studies met the inclusion criteria. The pooled prevalence of PPD in Iran was 25.3% (95% CI: 22.7%-27.9%). Amongst subgroups of unwanted delivery, illiterate, housewives, and having history of depression the prevalence was 43.4% (35.6-51.1), 31.6% (18.1-45.0), 30.7% (25.2-36.3), and 45.2% (35.4-53.1), respectively. Conclusions. Interventions that would specifically target women with a prior history of depression, illiterates, housewives, or women with unwanted pregnancies could be helpful to decrease the prevalence of postpartum depression in Iran.
Figures
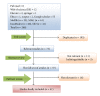
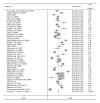
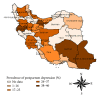
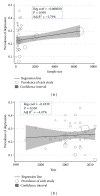

References
-
- Ahmed HM, Alalaf SK, Al-Tawil NG. Screening for postpartum depression using Kurdish version of Edinburgh postnatal depression scale. Archives of Gynecology and Obstetrics. 2011;285(5):1249–1255. - PubMed
-
- Al Dallal FH, Grant IN. Postnatal depression among Bahraini women: prevalence of symptoms and psychosocial risk factors. Eastern Mediterranean Health Journal. 2012;18(5):439–445. - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. Washington, DC, USA: American Psychiatric Press; 1994.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

