Acute abdominal pain secondary to chilaiditi syndrome
- PMID: 23936720
- PMCID: PMC3713330
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/756590
Acute abdominal pain secondary to chilaiditi syndrome
Abstract
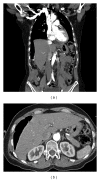
Chilaiditi syndrome is a rare condition occurring in 0.025% to 0.28% of the population. In these patients, the colon is displaced and caught between the liver and the right hemidiaphragm. Patients' symptoms can range from asymptomatic to acute intermittent bowel obstruction. Diagnosis is best achieved with CT imaging. Identification of Chilaiditi syndrome is clinically significant as it can lead to many significant complications such as volvulus, perforation, and bowel obstruction. If the patient is symptomatic, treatment is usually conservative. Surgery is rarely indicated with indications including ischemia and failure of resolution with conservative management.
Figures
References
-
- Kamiyoshihara M, Ibe T, Takeyoshi I. Chilaiditi's sign mimicking a traumatic diaphragmatic hernia. Annals of Thoracic Surgery. 2009;87(3):959–961. - PubMed
-
- Orangio GR, Fazio VW, Winkelman E, McGonagle BA. The Chilaiditi syndrome and associated volvulus of the transverse colon. Diseases of the Colon & Rectum. 1986;29(10):653–656. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources