miR156- and miR171-binding sites in the protein-coding sequences of several plant genes
- PMID: 23936788
- PMCID: PMC3727082
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/307145
miR156- and miR171-binding sites in the protein-coding sequences of several plant genes
Abstract
We identified the interaction sites of several miRNAs with the mRNAs from paralogs and orthologs of the SPL and HAM genes in A. thaliana. miRNAs from the miR156 and miR157 families in A. thaliana are shown to have binding sites within the mRNAs of SPL genes. The ath-miR156a-j binding sites located in the mRNAs of the SPL paralogs contain the sequence GUGCUCUCUCUCUUCUGUCA. This sequence encodes the ALSLLS motif. miR157a-d bind to mRNAs of the SPL family at the same site. We suggest merging the miR156 and miR157 families into one family. Several SPL genes in eight plants contain conserved miR156 binding sites. GUGCUCUCUCUCUUCUGUCA polynucleotide is homologous in its binding sites. The ALSLLS hexapeptide is also conserved in the SPL proteins from these plants. Binding sites for ath-miR171a-c and ath-miR170 in HAM1, HAM2, and HAM3 paralog mRNAs are located in the CDSs. The conserved miRNA binding sequence GAUAUUGGCGCGGCUCAAUCA encodes the ILARLN hexapeptide. Nucleotides within the HAM1, HAM2, and HAM3 miRNA binding sites are conserved in the mRNAs of 37 orthologs from 13 plants. The miR171- and miR170-binding sites within the ortholog mRNAs were conserved and encode the ILARLN motif. We suggest that the ath-miR170 and ath-miR171a-c families should be in one family.
Figures
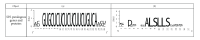

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

