The variable origin of the recurrent artery of Heubner: an anatomical and morphometric study
- PMID: 23936853
- PMCID: PMC3722790
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/873434
The variable origin of the recurrent artery of Heubner: an anatomical and morphometric study
Abstract
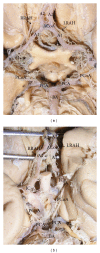
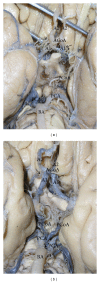
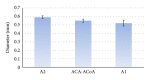
The recurrent artery of Heubner (RAH) is the largest vessel of the medial lenticulostriate arteries. It supplies many deep structures, mainly the corpus striatum, the globus pallidus, and the anterior crus of the internal capsule. The aim of the present paper was studying the morphological variations of the RAH and its diameter in relation to different areas of origin. The series contained the records from 183 formalin-fixed adult human brains. The calibrated digital images of the studied brains were evaluated and measured by Image J, which can calculate the number of pixels and convert them to metric measures. The RAH arose most often from the postcommunicating part of the anterior cerebral artery (47.81%). It originated from the precommunicating part of the anterior cerebral artery in 3.55% and at the level of the anterior communicating artery in 43.4% of cases. The RAH was missing in 5.19% and doubled in 6.28% of cases. The mean outer diameter of the RAH was 0.6 mm. The maximal measured diameter was 1.34 mm, and the minimal diameter was 0.19 mm. The awareness of the various anatomical and morphometric variations of the RAH is essential in planning the neurosurgical procedures to avoid unexpected neurological complications.
Figures

References
-
- Haroun RI, Rigamonti D, Tamargo RJ. Recurrent artery of Heubner: Otto Heubner’s description of the artery and his influence on pediatrics in Germany. Journal of Neurosurgery. 2000;93(6):1084–1088. - PubMed
-
- Loukas M, Louis RG, Jr., Childs RS. Anatomical examination of the recurrent artery of Heubner. Clinical Anatomy. 2006;19(1):25–31. - PubMed
-
- Zunon-Kipré Y, Peltier J, Haïdara A, et al. Microsurgical anatomy of distal medial striate artery (recurrent artery of Heubner) Surgical and Radiologic Anatomy. 2012;34:15–20. - PubMed
-
- Terminologia Anatomica: International Anatomical Terminology. New York, NY, USA: Thieme Medical Publishers; 1998. (Federative Committee on Anatomical Terminology (FCAT)).
-
- Standring S, editor. Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical basis of Clinical Practice. 39th edition. New York, NY, USA: Elsevier, Churchill Livingstone; 2005.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

