"Rescue" ablation of electrical storm in arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy in pregnancy
- PMID: 23937302
- PMCID: PMC3751358
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2261-13-58
"Rescue" ablation of electrical storm in arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy in pregnancy
Abstract
Background: Radiofrequency ablation (RFCA) became a treatment of choice in patients with recurrent ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation, and appropriate interventions of implanted cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD), however, electrical storm (ES) ablation in a pregnant woman has not yet been reported.
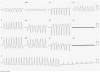
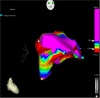
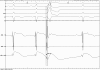
Case presentation: We describe a case of a successful rescue ablation of recurrent ES in a 26-year-old Caucasian woman during her first pregnancy (23rd week). The arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia/cardiomyopathy (ARVD/C) was diagnosed 3 years earlier and several drugs as well as 2 ablations failed to control recurrences of ventricular tachycardia. RFCA was performed on the day of the third electric storm. The use of electroanatomic mapping allowed very low X-ray exposure, and after applications in the right ventricular outflow tract, arrhythmia disappeared. Three months after ablation, a healthy girl was delivered without any complications. During twelve-month follow-up there was no recurrence of ventricular tachycardia or ICD interventions.
Conclusions: This case documents the first successful RFCA during ES due to recurrent unstable ventricular arrhythmias in a patient with ARVD/C in pregnancy. Current guidelines recommend metoprolol, sotalol and intravenous amiodarone for prevention of recurrent ventricular tachycardia in pregnancy, however, RFCA should be considered as a therapeutic option in selected cases. The use of 3D navigating system and near zero X-ray approach is associated with minimal radiation exposure for mother and fetus as well as low risk of procedural complication.
Figures
Comment in
-
Electrical storm in an adolescent with arrhythmogenic right ventricle cardiomyopathy treated with cardiac transplantation.Anatol J Cardiol. 2015 Jun;15(6):513. doi: 10.5152/akd.2015.5943. Epub 2015 May 22. Anatol J Cardiol. 2015. PMID: 26006146 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Zipes DP, Camm AJ, Borggrefe M, Buxton AE, Chaitman B, Fromer M, Gregoratos G, Klein G, Moss AJ, Myerburg RJ, Priori SG, Quinones MA, Roden DM, Silka MJ, Tracy C, Smith SC Jr, Jacobs AK, Adams CD, Antman EM, Anderson JL, Hunt SA, Halperin JL, Nishimura R, Ornato JP, Page RL, Riegel B, Priori SG, Blanc JJ, Budaj A, Camm AJ, Dean V, Deckers JW, Despres C, Dickstein K, Lekakis J, McGregor K, Metra M, Morais J, Osterspey A, Tamargo JL, Zamorano JL. American College of Cardiology. ACC/AHA/ESC 2006 guidelines for management of patients with ventricular arrhythmias and the prevention of sudden cardiac death: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force and the European Society of Cardiology Committee for Practice Guidelines (Writing Committee to Develop Guidelines for Management of Patients with Ventricular Arrhythmias and the Prevention of Sudden Cardiac Death) J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;48:e247–e346. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2006.07.010. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Szumowski L, Szufladowicz E, Orczykowski M, Bodalski R, Derejko P, Przybylski A, Urbanek P, Kuśmierczyk M, Koźluk E, Sacher F, Sanders P, Dangel J, Haissaguerre M, Walczak F. Ablation of severe drug-resistant tachyarrhythmia during pregnancy. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2010;21:877–882. - PubMed
-
- Makhija A, Sharada K, Hygriv Rao B, Tchachil A, Narsimhan C. Hormone sensitive idiopathic ventricular tachycardia associated with pregnancy: successful induction with progesterone and radiofrequency ablation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2011;22:95–98. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8167.2010.01797.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

